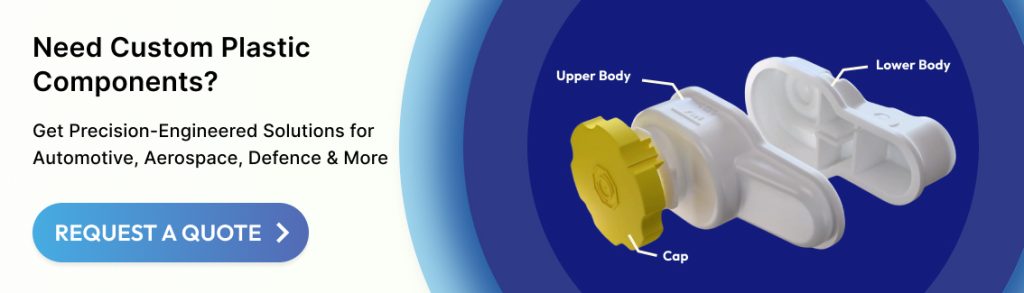
Choosing the wrong plastic moulding process risks your program timeline and budget. A flawed material selection can lead to field failures and warranty costs. These decisions impact your total cost of ownership and supply chain stability.
Procurement and engineering leaders must navigate these technical pitfalls strategically. Understanding moulding fundamentals is crucial for supplier evaluation and risk mitigation.
This guide explains key plastic moulding methods and performance metrics. You will learn common pitfalls and best practices for OEM sourcing.
Quick Look
- Moulding plastic success depends on aligning part design, material behavior, tooling strategy, and production controls early in the program lifecycle.
- Different moulding processes suit different risk profiles, volumes, tolerances, and regulatory exposure across automotive, EV, defence, and appliance programs.
- Tooling choices lock long-term cost, quality, stability, and scalability more than raw material prices or machine rates.
- Poor DfM and late supplier involvement cause most delays, rework costs, and PPAP failures in plastic moulding programs.
- Measuring TCO, cycle time, scrap rate, and dimensional stability gives you better supplier visibility than quoted part prices.
What Is Plastic Moulding and Why Does It Matter in Modern Manufacturing
Plastic moulding shapes polymers using a custom tool under heat and pressure. It is the dominant method for high-volume component manufacturing. OEMs select it for design freedom, weight reduction, and cost efficiency at scale. The process fundamentally determines your part quality and production scalability.
Your moulding choices directly influence launch timelines and lifecycle costs. Selecting the optimal method is a core procurement responsibility.
When you evaluate moulding strategy, you should consider how process selection impacts applications such as Earth Movers and Heavy Vehicle Components and Interior & Exterior Accessories and Components, where dimensional stability, surface finish, and material behavior directly affect compliance, durability, and production continuity.
JaiRaj Group integrates injection, blow, and rotational moulding with in-house tooling and process validation systems, allowing you to align geometry, material selection, and production scale within a single coordinated manufacturing framework.
Types of Plastic Moulding Processes
Plastic moulding is not a single technique. Each process serves distinct part geometries, volumes, and cost brackets. Misapplying a method increases unit cost and performance risk. Your choice balances tooling investment against production volume and part function.
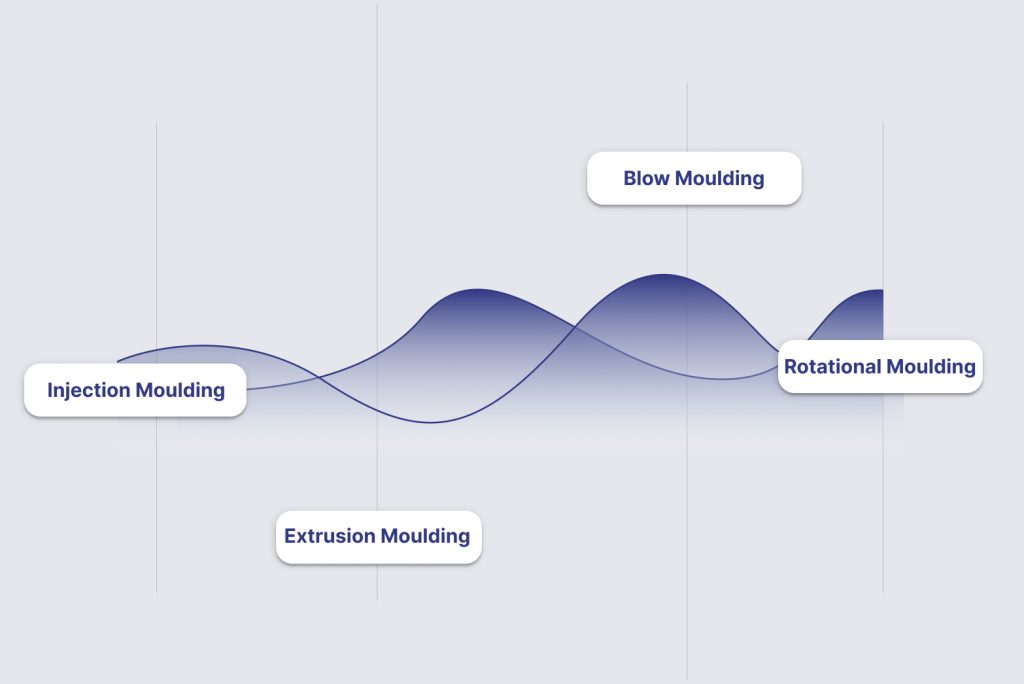
The primary industrial plastic moulding methods include:
- This process forces molten plastic into a high-pressure steel mould.
- It is best for high-volume parts with tight tolerances and complex details.
- Tooling costs are high, but per-part costs are very low at scale.
- Common applications include automotive dashboards, brake pedal assemblies, and appliance housings.
Blow Moulding
- Blow moulding inflates a plastic parison inside a hollow mould.
- It exclusively produces hollow parts like tanks, ducts, and bellows.
- The process offers good strength-to-weight for fluid containers.
- It fails if misused for solid parts or components requiring uniform wall thickness.
Rotational Moulding
- Rotational moulding uses a rotating mould to coat the interior with plastic.
- It creates stress-free, thick-walled, large parts like heavy vehicle body panels.
- Tooling costs are lower than injection moulding, but cycle times are longer.
- It is ideal for low-volume, large enclosures for earthmover components or defence applications.
Extrusion Moulding
- This process pushes plastic through a die to create continuous profiles.
- It manufactures pipes, seals, sheets, and solar panel structural components.
- Tooling is simple, but design is limited to consistent cross-sections.
- It is not suitable for discrete, three-dimensional parts.
Understanding each process clarifies the initial selection. The real complexity begins during the execution workflow.
Also read: Blow Molding vs Rotational Molding: Key Differences Explained
The Plastic Moulding Workflow in 5 Simple Steps
A disciplined workflow separates successful programs from delayed ones. Each stage introduces critical cost and timeline decisions. Skipping steps risks validation failures and production bottlenecks.
Follow these five core stages from design to stable production:
Step 1 – Part Design & Design for Manufacturability (DfM)
- DfM optimizes the part design for the chosen moulding process.
- It addresses draft angles, uniform wall thickness, and rib placement.
- Engineers often design parts that are difficult to eject or that warp.
- Poor DfM causes tooling rework, escalating costs and delaying trials.
Step 2 – Material Selection (How to Choose the Right Polymer)
- Material choice depends on mechanical, thermal, and chemical needs.
- Automotive, defence, and aerospace have strict compliance requirements.
- Do not simply choose the “strongest” or cheapest polymer available.
- Select materials like advanced nylon or PBT based on functional specs.
Step 3 – Tooling & Mould Development
- Mould development is the largest upfront investment and timeline driver.
- Decisions include single versus multi-cavity tools and steel grade.
- This phase locks in your part cost, quality ceiling, and production capacity.
- In-house tooling control, like at JaiRaj Group, mitigates timeline risk.
Step 4 – Trial Runs, Validation & PPAP
- T0/T1 trials produce the first samples for dimensional and functional checks.
- Quality teams validate parts against drawings and performance standards.
- This stage requires PPAP documentation for automotive OEMs.
- Delays here directly postpone your scheduled start of production (SOP).
Step 5 – Serial Production & Process Control
- Serial production focuses on cycle time optimization and scrap reduction.
- Consistent process control ensures every part meets specifications.
- Statistical process control (SPC) maintains dimensional stability.
- Process repeatability is key to managing your total cost of ownership.
A smooth workflow depends on tracking the right performance metrics. These numbers reveal your program’s true health.
4 Key Metrics That Define Success in Plastic Moulding
Move beyond unit price to measure moulding success strategically. These metrics quantify cost, efficiency, and quality performance. They provide data for supplier evaluations and program reviews.
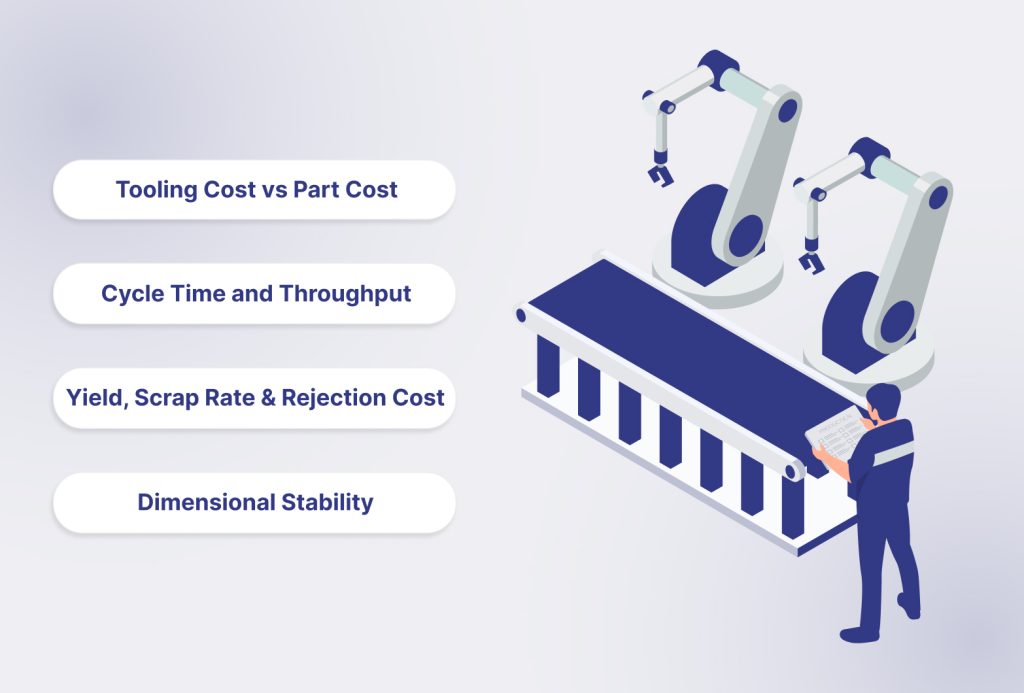
Monitor these four essential performance indicators:
Tooling Cost vs Part Cost (TCO Perspective)
- Amortize tooling cost over the lifetime volume of parts produced.
- A higher tooling investment often lowers the long-term piece price.
- Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) for accurate sourcing decisions.
Cycle Time and Throughput
- Cycle time is the number of seconds required to produce one moulding cycle.
- It directly determines your production capacity and per-part cost.
- Part design, material flow, and machine efficiency influence this metric.
Yield, Scrap Rate, and Rejection Cost
- Scrap rate is the percentage of non-conforming parts in a production run.
- Calculate it to understand true manufacturing efficiency and cost.
- High scrap often indicates underlying design or process control issues.
Dimensional Stability and Quality Consistency
- Measure process capability (Cpk) to quantify production consistency.
- It shows how reliably parts stay within specification limits.
- Quality drifts over time without rigorous process control and monitoring.
Ignoring these metrics leads to predictable and costly mistakes. Learn to recognize and avoid these common errors.
Common Mistakes in Plastic Moulding and How to Avoid Them
Procurement and program managers often encounter these avoidable pitfalls. Each mistake escalates costs, delays launches, or introduces quality failures. Recognizing them early protects your program.
Avoid these four critical errors in your moulding projects:
Designing Without Manufacturing Input
- Engineering designs in isolation often create un-mouldable part features.
- This leads to expensive tool rework and delayed trial schedules.
- Solution: Implement Early Supplier Involvement (ESI) for DfM reviews.
Choosing Material Based Only on Cost
- Selecting the cheapest polymer often compromises part performance.
- This risk leads to field failures, warranty claims, and compliance gaps.
- Solution: Define performance requirements first, then source cost-optimal materials.
Underestimating Tooling Lead Times
- Tooling development typically takes 12-20 weeks for complex moulds.
- Ignoring this timeline jeopardizes your program’s SOP date.
- Solution: Integrate tooling development into your critical path at program kick-off.
Single-Supplier Dependency Risks
- Relying on one vendor creates vulnerability during capacity shocks.
- A lack of process maturity at the supplier compounds this risk.
- Solution: Partner with suppliers offering multi-plant support and proven process control.
Facing these challenges in your current supply chain requires evaluating structural resilience rather than reacting during disruption. JaiRaj Group supports multi-plant execution across automotive and industrial programs, including Roto Moulding Components and Solar Plastic Components, where coordinated tooling control and standardized process validation strengthen supply continuity across locations.
Adopting industry best practices proactively prevents these mistakes. They build a foundation for reliable, scalable production.
Also read: PP vs PVC: Understanding Performance and Application Differences
Best Practices for Reliable, Scalable Plastic Moulding
Incorporate these proven practices into your sourcing and development strategy. They enhance cost predictability, ensure quality, and accelerate time-to-market. These methods separate strategic partners from basic vendors.
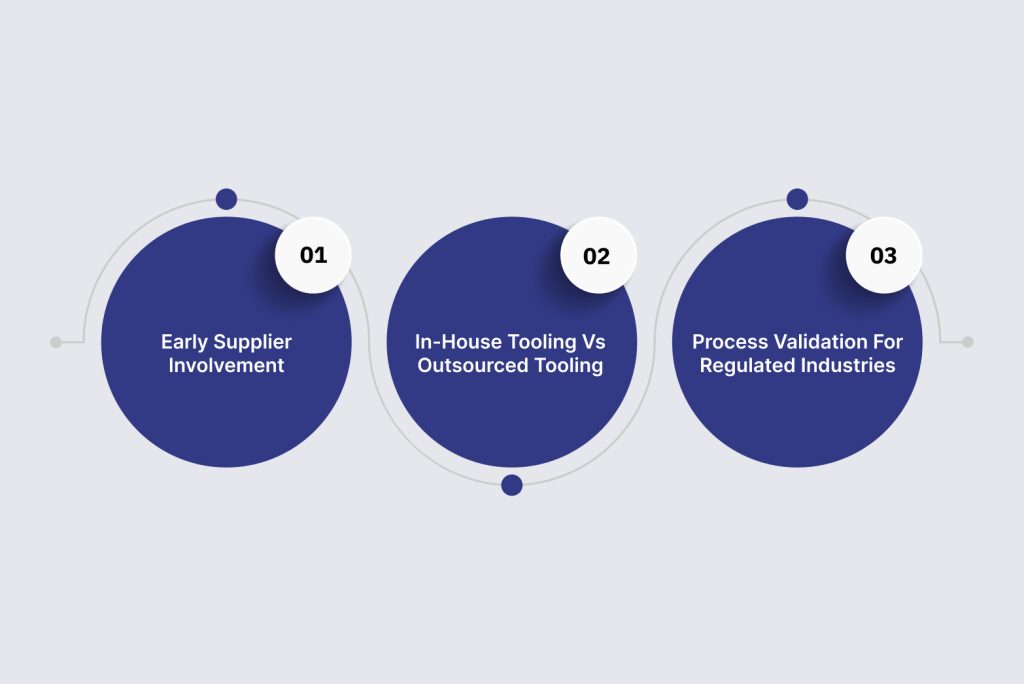
Implement these three essential best practices:
Early Supplier Involvement (ESI)
- Involve your moulding partner during the component design phase.
- This collaboration identifies and solves manufacturability issues early.
- Impact: ESI reduces tooling rework costs and prevents launch delays.
In-House Tooling vs Outsourced Tooling
- Suppliers with in-house tooling have direct control over mould quality and timing.
- Outsourcing tooling adds a supply chain layer and potential delays.
- Impact: In-house capability, like JaiRaj’s, provides better timeline certainty and cost control.
Material and Process Validation for Regulated Industries
- Automotive, defence, and aerospace require rigorous validation protocols.
- This includes PPAP, first article inspection, and material certifications.
- Impact: Thorough validation ensures compliance and prevents late-stage qualification failures.
These practices form the basis for evaluating a capable manufacturing partner. Use a structured checklist for your next supplier assessment.
How to Evaluate a Plastic Moulding Partner
Your moulding partner’s capabilities directly affect your program’s success. Use this checklist during your RFQ process and facility audits. It covers the essential technical and strategic competencies.
- Process Coverage: Does the partner offer injection, blow, rotational, and extrusion moulding?
- Tooling Capability: Do they develop moulds in-house with full design support?
- Material Depth: Can they process engineering polymers like Nylon, PBT, and POM?
- Quality Systems: Are they certified to IATF 16949, ISO 9001, and ISO 14001?
- Program Management: Do they have dedicated teams for launch and serial life management?
- Risk Mitigation: Do they operate multiple facilities to ensure supply continuity?
A partner excelling in these areas becomes a strategic asset. They bring technical expertise and operational stability to your supply chain.
How JaiRaj Group Approaches Plastic Moulding for OEMs
OEMs face tight deadlines, complex part designs, and stringent quality mandates. Sourcing from fragmented suppliers increases coordination risk and cost volatility. You need a partner that consolidates expertise and ensures seamless execution.
JaiRaj Group acts as a single-point solution for precision plastic components. We integrate deep engineering with multi-process manufacturing. Our approach reduces your program risk from design to delivery.
- Multi-Process Expertise: We operate injection, blow, rotational, and extrusion lines. This ensures process selection is based on your needs, not vendor limitations. We apply the optimal method for Solar Plastic Components, Mobility Plastic Base Seating Solutions, and complex assemblies.
- In-House R&D & Tooling: Our development centers design parts and build moulds internally. This controls quality, cost, and timelines for precision components and specialized items like Plastic Bellows & Struts.
- Cross-Industry Validation: Our components serve automotive, defence, aerospace, and EV mobility. This experience meets diverse compliance standards like PPAP, ensuring reliability from consumer appliances to defence platforms.
- Multi-Plant Network: Facilities in Manesar, Sanand, and Aurangabad provide supply resilience. This mitigates your risk from single-location dependency and supports just-in-time delivery.
JaiRaj Group delivers a strategic manufacturing partnership for scaled production.
Also read: How to Choose the Right Injection Molding Supplier
Conclusion
Plastic moulding is a fundamental pillar of modern manufacturing. Your mastery of its methods, metrics, and pitfalls controls cost and quality. It ensures on-time launches and long-term supply chain stability.
JaiRaj Group combines four decades of expertise with a full-service manufacturing model. We produce critical components from plastic bellows and seating solutions to heavy vehicle panels. Our capabilities turn complex moulding challenges into reliable production outcomes.
Reach out to JaiRaj Group to discuss your requirements.
FAQs
Q. What is the most cost-effective plastic moulding method?
Injection moulding is most cost-effective for high-volume production. Its high tooling cost spreads over thousands of parts. Rotational moulding has lower tooling cost for large, low-volume items.
Q. How long does plastic moulding tooling take?
Tooling development typically requires 12 to 20 weeks. Complexity, steel availability, and approval cycles influence this timeline. In-house tooling shops can often provide better schedule certainty.
Q. How do I choose between injection and rotational moulding?
Choose injection moulding for complex, high-volume parts with tight tolerances. Select rotational moulding for large, hollow, or thick-walled components at lower volumes. Part geometry and annual quantity dictate the choice.
Q. What affects plastic moulding cost the most?
Tooling amortization and raw material costs have the largest impact. Cycle time and scrap rate then determine the ongoing production cost. Design complexity drives all these factors.
Q. Is plastic moulding suitable for safety-critical components?
Yes, with the correct material, validation, and process control. Automotive braking system components and aerospace interiors use moulded plastics. They must meet strict standards like IATF 16949.