From passenger cars to electric vehicles, plastics are now integral to automotive design. By 2026, global automotive plastics demand is projected to exceed USD 30.8 billion, driven by lightweighting, fuel efficiency, and electrification goals.
Plastics help manufacturers reduce vehicle weight, improve durability, and enhance design flexibility, all while cutting production costs.
This article explains why car plastics dominate the automotive sector, the key types used, how to choose the right material, and what the future holds for plastics in automotive applications.
Key Takeaways:
- Car plastics reduce vehicle weight, improving fuel efficiency and EV range.
- They resist corrosion, chemicals, and extreme temperatures for long-lasting performance.
- Key types include Polypropylene, PVC, ABS, Polycarbonate, Polyurethane, Polyethylene, Nylon, POM, TPO/TPE, and PP-EPDM.
- Used in bumpers, dashboards, trims, fuel systems, seating, suspension, and interior/exterior components.
- Selection depends on mechanical requirements, thermal stability, chemical exposure, cost, and production volume.
Before reviewing specific plastics, it is important to understand why manufacturers increasingly rely on them.
Why Plastics Are Preferred in Automotive Manufacturing?
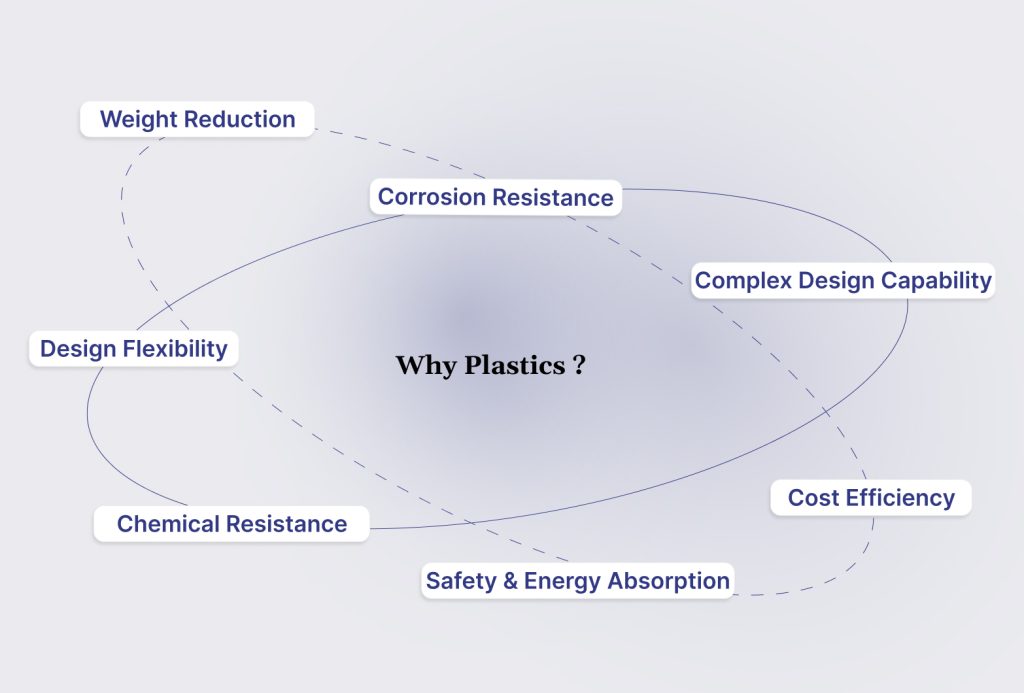
Car plastics are a core enabler of modern vehicle design, offering lightweighting, durability, and cost efficiency while supporting safety, performance, and sustainability targets.
For OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers, plastics are not just a material choice, they are a strategic solution that enhances manufacturability and program reliability.
Here’s why manufacturers consistently rely on plastics in automotive applications:
- Weight Reduction: Vehicles with higher plastic content weigh less, improving fuel efficiency and lowering CO₂ emissions. Lightweighting is especially critical for EVs, where every kilogram affects battery range.
- Corrosion Resistance: Plastics resist rust, salt, and chemical exposure, increasing component lifespan and reducing maintenance compared with metals.
- Complex Design Capability: Plastics enable the integration of multiple features into a single molded part, reducing assembly steps, part count, and potential failure points.
- Cost Efficiency: Injection molding and other plastic processing methods lower manufacturing costs, particularly for high-volume production.
- Safety and Energy Absorption: Materials such as glass-reinforced polyamides and TPO can absorb impact energy, enhancing occupant safety in crash scenarios.
- Thermal and Chemical Resistance: Automotive plastics withstand extreme temperatures, oils, and chemicals, making them ideal for under-hood and fuel system components.
- Design Flexibility and Aesthetics: Plastics allow smooth surfaces, complex textures, and color customization, supporting both functional and cosmetic requirements in interiors and exteriors.
Ensure high-performance automotive components with JaiRaj Group’s expertise in car plastics, precision molding, and advanced polymer solutions trusted by OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers across India. Contact here.
With these advantages in mind, car plastics have become essential to modern automotive applications.
Top 10 Car Plastics Used in Automotive Applications
Car plastics are no longer just fillers in vehicles, they’re key to performance, safety, and efficiency. Automakers choose each material carefully to meet mechanical, thermal, and cost requirements.

Here’s a breakdown of the most essential car plastics and where they are used.
1. Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is a go-to material for high-volume automotive applications, prized for its lightweight profile and adaptability in both structural and cosmetic parts.
Key Properties: Light, impact-absorbing, chemical-tolerant, heat-stable
Common Applications: Bumpers, interior trims, battery housings, cable insulation, Plastic bellows & struts, Mobility plastic seating solutions
Unique Advantages:
- Retains shape under stress and temperature changes
- Helps achieve fuel efficiency through weight reduction
- Economical for large-scale manufacturing
- Performs well in areas exposed to chemicals or moisture
2. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
PVC combines affordability with versatility, making it ideal for interior components and seals that require safety and longevity.
Key Properties: Flame-retardant, thermally stable, cost-effective
Common Applications: Dashboard skins, wiring insulation, door panels, weather seals, Interior & exterior accessories, Hand Grips.
Unique Advantages:
- Available in rigid or soft formulations
- Maintains integrity under temperature fluctuations
- Easily molded into complex shapes
- Provides reliable protection for interior and exterior trims
3. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS is widely chosen for visible automotive components due to its toughness and ability to retain its finish under mechanical stress.
Key Properties: Tough, rigid, abrasion-tolerant
Common Applications: Dashboards, door trims, wheel covers, painted components, Brake & accelerator pedals, Shockers & suspension components .
Unique Advantages:
- Maintains structural integrity across temperature variations
- Excellent surface quality for aesthetic parts
- Resists scratches and wear from daily use
- Supports color customization and texturing
4. Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate is ideal for transparent or high-impact applications, offering strength and clarity in one material.
Key Properties: Strong, transparent, UV-stable
Common Applications: Headlamp lenses, display housings, exterior trims, Precision components from advanced polymers.
Unique Advantages:
- Retains clarity under prolonged sun exposure
- Absorbs shocks without cracking
- Maintains form in varying climates
- Suitable for high-visibility, safety-critical parts
5. Polyurethane (PUR)
Polyurethane is a versatile polymer used in both comfort-focused and mechanically demanding applications within vehicles.
Key Properties: Soft or firm, abrasion-proof, chemical-tolerant
Common Applications: Seat cushioning, headrests, insulation panels, suspension bushings
Unique Advantages:
- High elasticity for seating and cushioning
- Resists surface wear and chemical exposure
- Performs reliably under repeated mechanical loads
- Adaptable for comfort, structural, and insulation uses
6. Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene excels in protective and high-impact components, offering resilience where repeated stress occurs.
Key Properties: Tough, flexible, chemically tolerant
Common Applications: Fuel tanks, fender liners, splash guards, electrical insulation
Unique Advantages:
- Absorbs impacts and returns to original shape
- Lightweight yet strong for protective applications
- Handles exposure to fuels and other fluids
- Efficient for high-volume molding processes
Also Read: Plastic Injection Molding: Precision Thermoplastic Components
7. Polyamide (Nylon, PA)
Nylon is a high-performance engineering plastic capable of handling demanding mechanical and thermal conditions.
Key Properties: Strong, wear-proof, heat-tolerant
Common Applications: Engine components, gears, electrical connectors, under-the-hood parts, Braking System Components
Unique Advantages:
- Withstands continuous stress and high temperatures
- Retains precise shape and size over time
- Resistant to oils and fuels
- Ideal for high-load structural or mechanical components
8. Polyoxymethylene (POM or Acetal)
POM is a precision-grade plastic used where low friction, high stiffness, and dimensional accuracy are essential.
Key Properties: Stable, low-friction, stiff
Common Applications: Fuel system components, small gears, lock systems, door handles
Unique Advantages:
- Maintains tight tolerances over repeated cycles
- Reduces wear in moving parts
- Offers strength without bulk
- Suitable for precise mechanical assemblies
Also read: Automotive Interior & Exterior Plastic Parts Manufacturing: Trends and Innovations in 2025
9. Thermoplastic Olefin (TPO) and Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE, TPV)
Introduction: These polymers are ideal for exterior and interior components requiring a mix of rigidity and softness.
Key Properties: Semi-rigid, shock-absorbing, resilient
Common Applications: Bumper covers, interior skins, weather seals, protective trim
Unique Advantages:
- Combines structural integrity with soft-touch feel
- Can withstand impacts without permanent deformation
- Maintains appearance in visible areas
- Suitable for complex shapes and high-stress points
10. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer Modified Polypropylene (PP-EPDM)
PP-EPDM is engineered for exterior parts that require elasticity, durability, and repeated impact absorption.
Key Properties: Elastic, impact-recovering, weather-proof
Common Applications: Bumpers, exterior claddings, flexible trim parts
Unique Advantages:
- Returns to shape after repeated stress
- Performs well under sunlight and weathering
- Handles complex shapes and mounting requirements
- Ideal for high-stress exterior panels
Now that the top car plastics have been outlined, the next consideration is how to select the most suitable material for specific automotive components.
How to Choose the Right Plastic for Automotive Components?
Choosing the right plastic is a strategic decision that impacts part performance, safety, production efficiency, and program cost. The right material ensures components withstand mechanical stress, temperature variations, chemical exposure, and long-term wear while meeting regulatory and design requirements.
Consider the following factors when selecting plastics for automotive applications:
- Mechanical Requirements: Strength, stiffness, and impact resistance dictate whether a polymer or reinforced blend is necessary.
- Thermal and Environmental Exposure: Engine compartments require heat-resistant plastics, while exterior trims need UV-stable, weather-resistant materials.
- Cost vs. Volume: High-volume parts benefit from injection-molded PP or ABS, while specialized high-performance components may justify higher-cost engineering plastics.
- Processing Capability: Evaluate mold design, cycle time, and post-processing needs. Complex parts may require multi-material molding or reinforced composites.
- Weight Targets and Sustainability Goals: For EVs and hybrid vehicles, plastics that reduce mass without compromising strength or safety are critical.
Tip: Collaborate with partners like JaiRaj Group early to run material flow simulations, evaluate mechanical performance, and ensure compliance with IATF 16949 and ISO 14001 standards.
Also read: How to Choose the Right Plastic Product Supplier for Automotive & Industrial Components
Beyond material selection, understanding industry trends is essential.
Future of Car Plastics in the Automotive Industry
The future of car plastic is not just about material substitution; it’s about aligning engineering, sustainability, and digital manufacturing strategies to meet next-generation mobility demands.

As OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers, you redefine vehicle architectures, plastics will play a decisive role in enabling lighter, safer, and more sustainable designs while controlling costs and production complexity.
Key focus areas include:
- Sustainable and Recycled Materials: Automakers increasingly use recycled polymers, bio-based plastics, and post-industrial resins to meet ESG goals.
- Lightweighting for EVs: As EV adoption grows, reducing battery load through plastics will be a key engineering strategy.
- Advanced Composites: Carbon fiber-reinforced plastics and hybrid thermoplastics will replace traditional metals in structural and high-performance parts.
- Integration with Smart Manufacturing: IoT-enabled production and digital twins will optimize plastic part design, reducing cycle times, scrap, and supply chain risks.
- Enhanced Safety Features: Energy-absorbing and fire-retardant plastics will become standard in interiors, under-hood components, and structural elements.
Takeaway: Ensure reliable use of high-performance, sustainable car plastics in automotive production with proven design and processing expertise from JaiRaj Group.
For OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers, selecting the right plastics is only one part of the equation. Supplier expertise, process capabilities, and supply resilience are equally critical.
Strategic Solutions with Car Plastics For OEMs and Tier-1 Suppliers
For OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers, vehicle performance, reliability, and program efficiency hinge on selecting the right car plastics and leveraging supplier expertise.
Plastics now drive lightweighting, durability, cost efficiency, and design flexibility while supporting safety and sustainability targets.
JaiRaj Group enables strategic outcomes in automotive plastic applications through the following levers:
1) Material Selection for Performance and Reliability
With expertise across various plastics, JaiRaj helps OEMs balance impact resistance, mechanical strength, and thermal stability while managing cost and compliance.
Strategic Car Plastics and Applications:
- Polypropylene (PP): Bumpers, trims, battery housings, cable insulation
- PVC: Dashboards, wiring insulation, door panels, weather seals
- ABS / ABS + PC: Dashboards, door trims, wheel covers, painted components
- Polycarbonate (PC): Headlamp lenses, display housings, exterior trims
- Polyurethane (PUR): Seat cushioning, headrests, suspension bushings
- Polyethylene (PE): Fuel tanks, fender liners, splash guards
- Polyamide (Nylon, PA): Engine parts, gears, connectors, under-hood components
- Polyoxymethylene (POM): Door handles, fuel system components, small gears
- TPO / TPE / TPV: Bumper covers, interior skins, protective trims
- PP-EPDM: Flexible trims, bumpers, exterior claddings.
2) Design-for-Manufacturability and Tooling Integration
Early collaboration with in-house tooling and moulding teams, supported by simulation insights, ensures optimal part geometry, reduces rework, and accelerates program approval.
3) Application-Specific Process Solutions
Offering injection, blow, rotational moulding, extrusion, welding, and assembly under one roof, JaiRaj enables precise production for bumpers, dashboards, fuel system components, and interior trims with consistent quality and efficiency.
4) Supply Network and Production Resilience
Facilities in Faridabad, Manesar, Aurangabad, Sanand, and Rudrapur ensure proximity to India’s automotive hubs, shortening lead times, cutting logistics costs, and providing backup capacity during supply disruptions.
5) Proven Track Record for Automotive Programs
With 35+ years of experience and certifications including IATF 16949, ISO, and CE, JaiRaj delivers reliable car plastic solutions for interior & exterior components, structural parts, and precision assemblies. Their portfolio includes:
- Brake & Accelerator Pedals
- Mobility Plastic Seating Solutions
- Shockers & Suspension Components
- Plastic Bellows & Struts
- Interior & Exterior Accessories
- Precision Components from Advanced Polymers
For procurement leaders, JaiRaj Group delivers strategic solutions, ensuring performance, program continuity, and risk mitigation across high-volume automotive applications.
Conclusion
Car plastic plays a key role in modern automotive programs. It influences vehicle performance, safety, and overall production efficiency. For OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers, the objective goes beyond replacing traditional materials, it’s about selecting plastics that deliver reliability, cost control, and sustainability.
Companies that integrate car plastic effectively achieve three major benefits:
- Improved efficiency by reducing vehicle weight and enhancing fuel performance.
- Extended component life through resistance to temperature fluctuations, mechanical stress, and environmental wear.
- Optimized lifecycle cost by lowering production expenses, minimizing replacements, and supporting ESG objectives.
For teams developing new parts or upgrading existing ones, JaiRaj Group offers material expertise and plant visits in Manesar, Sanand, or Aurangabad.
Contact JaiRaj Group to explore car plastic solutions for your requirements.
FAQs
1. Why are plastics increasingly preferred over metals in automotive parts?
Plastics reduce weight, improve corrosion resistance, allow complex designs, and lower manufacturing costs compared to metals.
2. Which plastics are commonly used for exterior automotive parts?
Polypropylene (PP), ABS/PC blends, and polycarbonate (PC) are commonly used for bumpers, trims, and lighting components.
3. How does plastic help in EV efficiency?
Lightweight plastics reduce vehicle mass, directly improving battery range and reducing energy consumption.
4. Can plastics be used in engine and high-temperature areas?
Yes, reinforced nylons (PA6-GF, PA66-GF) and polyesters (PBT, PET) can withstand high temperatures under the hood.
5. Are recycled plastics viable for automotive use?
Recycled and bio-based plastics are increasingly used in non-critical components, meeting sustainability targets without compromising quality.
6. How do suppliers influence plastic part performance?
Suppliers offering early-stage simulation, DfM insights, and validated molding processes ensure dimensional stability, structural integrity, and faster SOP launches.