Is PBT plastic really safe, or are there hidden risks? Today, materials are expected to deliver both high performance and safety. Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) is no exception. The global PBT market will reach USD 5.5 billion by 2035, showing just how important this material has become across industries.
Known for its strength and reliability, PBT is widely used in automotive, electrical, and industrial applications. However, as its use grows, so do questions about its safety and potential toxicity.
Many manufacturers and suppliers want to know whether PBT poses risks during production or disposal, and how to manage them effectively. In this blog, you’ll explore what makes PBT such a valuable material, the safety concerns you should be aware of, and the best practices for handling it responsibly.
Key Takeaways:
- In its solid, finished form, PBT plastic is stable and safe to use in automotive, electrical, and industrial products, with very low toxicity risks.
- During manufacturing or when PBT plastic is not disposed of properly, it can release harmful fumes and chemicals.
- PBT meets major global safety standards like RoHS and REACH, which means it doesn’t contain harmful substances and is safe for end users across regulated industries.
- To maintain safety during production, proper ventilation, the use of protective gear, and careful storage are important.
- PBT alternatives such as Nylon, Polycarbonate, or Polypropylene might be a better fit when factors like cost, flexibility, or impact strength are more important.
What is PBT Plastic?
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) is a strong, high-quality plastic that is considered a reliable choice for parts that need to last even in tough conditions.
PBT stands out for its balance of rigidity and toughness. This makes it ideal for use in automotive components such as Plastic Bellows & Struts, as well as electronics and industrial applications.
It performs well in demanding environments where materials are exposed to high temperatures, chemicals, or constant stress. Once you understand what PBT plastic is, it’s natural to wonder whether it poses any health or safety risks.
What Makes PBT Plastic a Preferred Choice?
PBT stands out for its dimensional stability under stress and its resistance to wear in tough environments. This durability ensures components perform reliably over time, making it a go-to material for producing long-lasting, high-performance parts. Key features include:
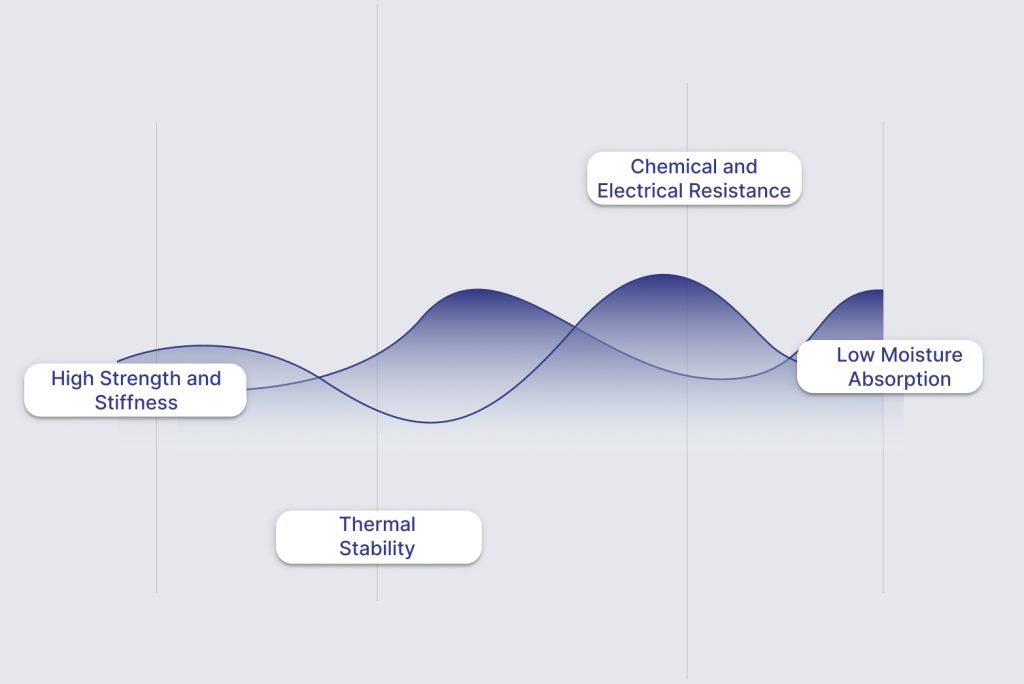
- High Strength and Stiffness: PBT maintains its shape and strength even under heavy loads. This makes it ideal for demanding parts, such as those in vehicles and machinery, that need to remain reliable over time.
- Chemical and Electrical Resistance: It withstands many harsh chemicals and is an excellent electrical insulator. That’s why it’s often used in electrical connectors and other sensitive components.
- Low Moisture Absorption: Because PBT absorbs little moisture, it maintains its strength and dimensions even in humid conditions. This helps it stay stable and dependable in different environments.
- Thermal Stability: PBT can withstand high temperatures up to about 150°C without breaking down. This makes it an excellent fit for parts exposed to heat, such as those near engines or in hot industrial environments.
Ensure reliable performance in critical automotive and industrial components, such as Precision Components from Advance Polymers or Braking System Components, with JaiRaj Group’s precision-engineered solutions and proven manufacturing expertise.
Where You’ll Find PBT Plastic in Everyday Use?
PBT’s toughness, flexibility, and environmental resistance make it useful across many industries. You’ll see it often in automotive, electronics, and heavy machinery.
- Automotive: You’ll find PBT in under-the-hood components, electrical connectors, and interior parts like dashboards and trims. Its ability to resist both heat and chemicals makes it ideal for these uses.
- Electrical & Electronics: With its excellent insulating properties, PBT is a popular choice for plugs, connectors, switches, and other electronic parts that require safety and reliability.
- Industrial Components: PBT’s rigidity and wear resistance make it ideal for mechanical parts that experience regular motion or heavy loads, such as gears, bearings, and other precision components.
Seeing how commonly PBT plastic is used in everyday products naturally leads to questions about its safety and potential health impact.
Is PBT Plastic Really Toxic?
PBT is a type of polyester made by combining terephthalic acid (TPA) with 1,4-butanediol. Like most thermoplastics, PBT’s health or environmental risks come mainly from how it’s made or disposed of. In regular use, it remains stable and safe.
Once PBT is in its solid, finished form, it’s generally safe and stable for most applications. Keep in mind that:
- PBT is safe for use in automotive, electrical, and industrial parts. It stays stable, absorbs little moisture, and doesn’t release harmful chemicals during regular use.
- PBT complies with global standards such as RoHS and REACH, ensuring it’s free of hazardous substances that could harm people or the environment.
While PBT plastic is generally considered safe in use, certain risks can arise during its production and disposal stages.
Potential Risks During Production and Disposal
PBT is safe when used in finished automotive parts such as Shockers & Suspension Components and Braking System Components. However, risks can arise during its production and disposal, leading to possible emissions or chemical exposure.
Keep these things in mind:
- Manufacturing Exposure: During production, workers might come into contact with raw materials that can irritate the skin or cause breathing issues. Using protective gear and keeping the workspace well-ventilated helps lower these risks.
- Disposal Concerns: PBT, when not handled properly, especially when burned, it can release harmful compounds like dioxins and furans. Recycling or disposing of it through approved facilities is the safest way to protect people and the environment.
Once you understand the potential risks during production and disposal, it shows the importance of following proper safety practices in manufacturing environments.
Suggested Read: 9 Types of Plastics Used in the Semiconductor Industry
Simple Safety Practices When Working with PBT in Manufacturing Environments
When working with PBT plastic in manufacturing, it’s crucial to prioritize worker safety and follow proper industry standards. PBT is a high-performance plastic widely used in automotive, electrical, and industrial applications; however, it must be handled with care.
Here are some safety tips to be followed:

Ventilation and Air Quality Control
When PBT is molded or extruded, the high processing temperatures can release fumes that may be harmful if not properly managed. Keeping the workspace air clean and safe is essential.
- Ensure proper ventilation: Install local exhaust systems near molding machines to capture and remove fumes right at the source.
- Use air filtration systems: High-efficiency filters help reduce airborne contaminants and maintain good air quality throughout the facility.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Workers involved in PBT manufacturing must wear the right protective gear to stay safe from heat, fumes, and particles. Here are the key PPE essentials:
- Heat-resistant gloves: Protect hands when handling hot parts or tools after molding.
- Respirators with filters: Prevent inhalation of fumes or fine plastic particles during processing.
- Protective eyewear: Shield eyes from splashes, dust, or heated plastic fragments.
Safe Handling and Storage
Proper handling and storage of PBT pellets before processing are essential to maintain their quality and prevent molding issues. Follow these best practices:
- Moisture-controlled storage: Keep materials in dry environments to prevent water absorption that can cause defects.
- Use drying equipment: Remove any residual moisture from PBT pellets before molding to ensure consistent product quality.
Temperature Control
Maintaining accurate temperature settings during PBT molding and extrusion is critical for both product performance and worker safety.
- Monitor temperature closely: Regularly check machine settings to prevent overheating or thermal degradation.
- Automatic shutoffs: Equip machines with automatic shutoff systems to reduce risks of overheating and potential fire hazards.
Chemical Safety and Disposal
Although PBT is stable, some additives or processing chemicals may require special care. Managing these substances safely ensures compliance and protects the environment.
- Review Safety Data Sheets (SDS): Always refer to SDS for proper handling, storage, and emergency procedures for all chemicals used.
- Responsible recycling and disposal: Dispose of waste materials in accordance with local environmental regulations and recycling protocols.
Fire Safety
Like many thermoplastics, PBT can ignite if exposed to high heat or open flames. Fire safety precautions are vital in any production setup.
- Accessible fire extinguishers: Keep extinguishers near high-temperature molding or extrusion stations.
- Regular fire drills: Conduct routine drills so all employees know exactly what to do in case of a fire emergency.
Training and Awareness
Proper training ensures every worker understands how to handle PBT safely and respond effectively to potential hazards.
- Continuous training: Offer regular sessions to keep employees up to date on safety practices and new handling techniques.
- Onboarding programs: Ensure new team members receive thorough safety and material-handling training before starting on the production floor.
JaiRaj Group helps OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers make informed choices by focusing on key strategic factors that drive performance, durability, and compliance in automotive manufacturing.
Whether selecting PBT or exploring alternatives, JaiRaj ensures that the material choice aligns with both technical and business goals for optimal results in production.
Exploring Safer and More Sustainable Alternatives to PBT Plastic
As manufacturing technologies advance and sustainability becomes a greater focus, OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers are exploring alternative materials. These materials can match or even outperform PBT in key areas, such as cost, performance, and eco-friendliness.
Below are a few alternatives to PBT plastic.
Nylon (PA)
Nylon, especially Nylon 6 and Nylon 66, is one of the most popular alternatives to PBT thanks to its strong mechanical properties and toughness.
- Advantages: Nylon offers better abrasion resistance and flexibility than PBT. It performs well under high stress, making it great for parts that experience friction or movement.
- Drawbacks: The main limitation of nylon is its tendency to absorb moisture. This can affect its shape and strength over time, particularly in humid conditions.
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate is another widely used engineering plastic, valued for its impact resistance and transparency. It’s common in both automotive and electrical applications.
- Advantages: PC has excellent impact strength and can handle extreme temperatures. It’s often used in lighting systems, displays, and protective housings where clarity and toughness are needed.
- Drawbacks: While PC is very strong, it’s more expensive than PBT and scratches more easily under rough handling.
Polypropylene is a cost-effective material known for its chemical resistance and versatility. Many OEMs choose it when they need a durable yet affordable plastic.
- Advantages: PP absorbs very little moisture, resists most chemicals, and is inexpensive. It’s especially popular for automotive interiors like dashboards, trims, and panels.
- Drawbacks: Although it’s strong and lightweight, PP lacks the dimensional stability of PBT and can deform at high temperatures.
Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS)
PPS is a high-performance plastic used in industries where parts must withstand extreme heat and harsh chemicals, such as automotive and aerospace manufacturing.
- Advantages: It offers exceptional chemical resistance, maintains its shape well, and can withstand temperatures up to 260°C.
- Drawbacks: PPS is more expensive than PBT and requires specialized machinery for processing, which can make production more complex.
Thermoplastic Polyester Elastomers (TPE-E)
When flexibility and strength are equally important, TPE-E can be a strong alternative to PBT. It’s used in automotive and industrial parts that need to stretch or bend without breaking.
- Advantages: TPE-E combines the elasticity of rubber with the strength and easy processing of plastics, making it perfect for flexible yet durable components.
- Drawbacks: TPE-E doesn’t handle heat as well as PBT and can be more expensive for large-volume manufacturing.
Knowing about possible alternatives to PBT is helpful, but it’s equally important to understand the regulations that govern its use and safety standards.
Also Read: 10 Best Car Plastics in the Automotive Industry You Need to Know
Key Regulations You Should Know About PBT
As PBT remains a key material across different sectors, OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers must remain compliant with global regulations focused on safety, environmental protection, and product reliability.
Below are the PBT plastic regulations you should know about.
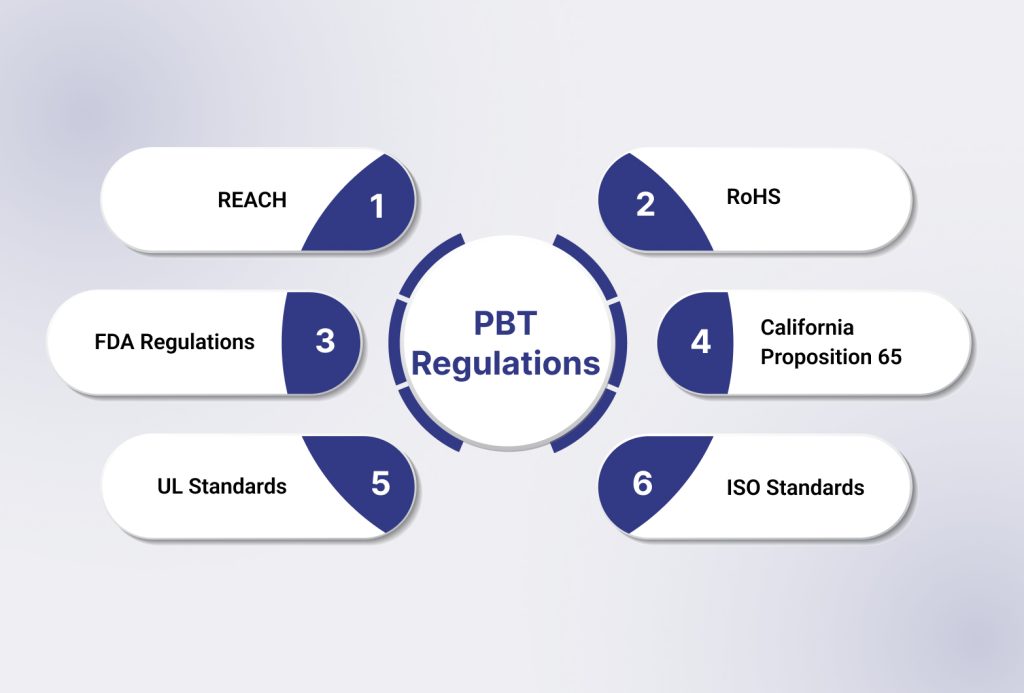
REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals)
The European Union’s REACH regulation is one of the toughest environmental laws affecting manufacturers that use PBT. It requires all chemicals, including plastics, to be registered with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA).
PBT must be tested to ensure it’s free from restricted chemicals such as phthalates or heavy metals. Manufacturers also need to maintain proper documentation and update safety data whenever new information emerges.
RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances)
The RoHS directive, also from the EU, limits the use of hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and hexavalent chromium in electrical and electronic equipment.
When PBT is used in components like automotive connectors, wiring, or electrical housings, it must comply with RoHS restrictions to ensure that no banned substances are present.
FDA Regulations (For Food Contact Materials)
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees materials that come into contact with food. While PBT isn’t typically used for food packaging, certain grades can be approved for specific applications, such as food processing equipment.
To be FDA-compliant, PBT must undergo strict testing to ensure it doesn’t release harmful chemicals into food during use. Manufacturers working in the food or consumer goods industries must verify that their PBT materials meet FDA safety standards.
California Proposition 65 (Prop 65)
Proposition 65 in California requires businesses to provide warnings if their products contain chemicals known to cause cancer, birth defects, or reproductive harm.
If any PBT component sold in California contains listed chemicals above the permitted limit, it must include a clear warning label. To stay compliant, manufacturers need to regularly test and certify their materials.
UL (Underwriters Laboratories) Standards
UL is a global safety certification body that tests and certifies materials for electrical and electronic applications. PBT used in these systems must meet UL’s fire and safety standards.
For example, PBT used in electrical connectors and circuit components must meet UL 94-V0 flame retardancy standards, ensuring the material doesn’t ignite easily under heat.
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) Standards
ISO standards help ensure quality, safety, and environmental responsibility throughout the manufacturing process. For companies working with PBT, ISO 9001 (quality management) and ISO 14001 (environmental management) are the most relevant.
Manufacturers must allow consistent product quality, safe production processes, and environmentally sound practices to meet ISO requirements.
Must Read: Plastic Parts in Automotive Manufacturing Trends & Challenges
How to Choose the Right Plastic Material for Automotive Manufacturing?
Choosing the right plastic materials plays a big role in making vehicles that are strong, reliable, and cost-efficient. At JaiRaj Group, we’ve built our expertise around delivering precision-engineered plastic solutions for the automotive, mobility, EV, and heavy equipment sectors.
With our advanced facilities in Faridabad, Rudrapur, Aurangabad, Manesar, and Sanand, we create high-quality components that meet the performance needs of modern automotive manufacturing.
Why choose Jairaj Group?
- Plastic Bellows & Struts, Hand Grips & Mobility Solutions: We manufacture flexible and durable parts for automotive and mobility applications using blow molding and extrusion molding technologies. These components are designed to perform well even under constant movement and pressure.
- Precision Components from Advanced Polymers: Our high-performance parts, made from materials like PEEK and polycarbonate, are ideal for demanding automotive environments. They withstand extreme temperatures, wear, and tough operating conditions.
- Roto-Moulded Components: We produce strong, long-lasting components through rotational molding, a process that delivers excellent structural integrity for engineering and automotive applications.
- Braking System Components: Using injection molding, we create braking system parts that meet strict industry standards. These components offer outstanding durability and thermal resistance, making them reliable even in high-stress situations.
- Advanced Materials Like TPE, TPU, and Nylon: TPE/TPU and Nylon are used in our production of dust covers, fuel line connectors, and general assembly parts. Their high strength and chemical resistance make them a trusted choice in automotive manufacturing.
Partner with JaiRaj Group for plastic components that enhance efficiency, durability, and reliability. With over 35 years of experience, we continue to deliver solutions that exceed expectations, powering progress in automotive and heavy equipment manufacturing.
Final Thoughts
PBT plastic is safe for use in automotive, electrical, and industrial applications when handled properly and according to safety standards. However, risks can occur during manufacturing or disposal if it’s exposed to high heat or not managed correctly. This can cause the release of harmful fumes or chemicals.
To keep things safe, manufacturers must ensure that PBT complies with standards such as RoHS and REACH, which help protect both workers and the environment. At JaiRaj Group, we create precision-engineered plastic solutions using advanced injection molding and extrusion molding technologies.
Our range of products, including brake system components and high-performance polymers, is built to perform under the demanding conditions of the automotive, aerospace, and heavy equipment industries.
Connect with JaiRaj Group for reliable, high-performance plastic components that bring strength, precision, and consistency to your automotive manufacturing operations.
FAQs
1. Can PBT plastic be recycled?
Yes, it can. However, the recycling process depends on the specific type of PBT used. It’s always best to check with your local recycling center or a facility that handles engineering plastics to see if they accept PBT.
2. Is PBT plastic resistant to UV radiation?
PBT can handle some UV exposure, but it’s not fully UV-proof. If it’s left under the sun for long periods, it can start to degrade. To make it more durable outdoors, manufacturers often mix in UV stabilizers.
3. How does PBT compare to plastics like ABS or PVC in strength?
PBT generally performs better when it comes to handling heat and chemicals. That’s why it’s often used in demanding applications. ABS, on the other hand, is tougher against impacts, while PVC is usually the budget-friendly option.
4. What are the common molding methods for PBT?
PBT is mainly shaped using injection molding, but it can also be processed through blow molding or extrusion. Injection molding is the go-to method because it delivers precise, high-quality parts.
5. Does PBT plastic release harmful fumes when burned?
Yes, it can. When exposed to high heat or flames, PBT may release fumes like dioxins and furans, which can be harmful. That’s why it’s important to recycle or dispose of it safely and avoid burning it.