Choosing between polypropylene and other plastics is crucial for manufacturers, with the global PP market growing from $123.46 billion in 2022 to an expected $177.73 billion by 2030, reflecting its demand for lightweight, durable, and cost-effective applications.
For manufacturers, choosing polypropylene vs plastic goes beyond basic properties. Material costs, processing requirements, recyclability, and application-specific performance such as chemical resistance or thermal stability directly influence reliability and customer satisfaction.
This guide helps engineers and procurement teams evaluate polypropylene vs plastic, identify key decision factors, and select materials that ensure optimal product quality, manufacturing efficiency, and long-term value.
Key Takeaways:
Polypropylene (PP) is a lightweight, flexible, and chemical-resistant thermoplastic, widely used in packaging, automotive, and industrial applications.
Plastics are a broad category, including PE, PVC, ABS, PS, and others, each with different properties for varied uses.
PP provides durability, chemical resistance, and cost-efficiency, while other plastics may offer higher rigidity, heat tolerance, or specialized performance.
PP is generally economical, recyclable (#5), and energy-efficient; other plastics differ in cost, recyclability, and environmental impact.
Choose PP for lightweight, durable, chemically resistant needs, and other plastics when specific strength or specialized properties are required.
Before understanding Polypropylene vs plastic difference, let’s define polypropylene.
What is Polypropylene?
Polypropylene (PP) is a versatile polymer widely used in injection molding due to its lightweight nature, cost efficiency, and adaptability across industrial applications Its strength and chemical resistance make it ideal for components such as Brake & Accelerator Pedals and Shockers & Suspension Components in automotive applications.
For procurement leaders, program managers, and sourcing executives, understanding polypropylene’s uses, types, and products allows for more informed decisions across materials, tooling, and processes, balancing cost, resilience, and performance.
Key Applications of Polypropylene
To start, it’s important to recognize the breadth of polypropylene’s applications. Its combination of strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance makes it suitable for a wide range of industrial and packaging uses:
Protective Covers and Thermal Films: Beyond simple packaging, PP covers protect products from contamination or damage during storage and transit.
Industrial and Household Products: PP’s flexibility and durability make it ideal for containers, utensils, household items, and select industrial components, combining functionality with resilience.
Medical Applications: With sterilization capability and chemical resistance, PP supports medical needs including instrument parts, surgical covers, and other consumables, ensuring safety and compliance.
Automotive Components: Durable and lightweight, PP is used for Mobility Plastic Seating Solutions and Interior & Exterior Accessories, providing both structural integrity and aesthetic appeal.
The next consideration is understanding the different types of polypropylene, each offering unique properties to match program and sourcing requirements.
Types of Polypropylene and Their Benefits
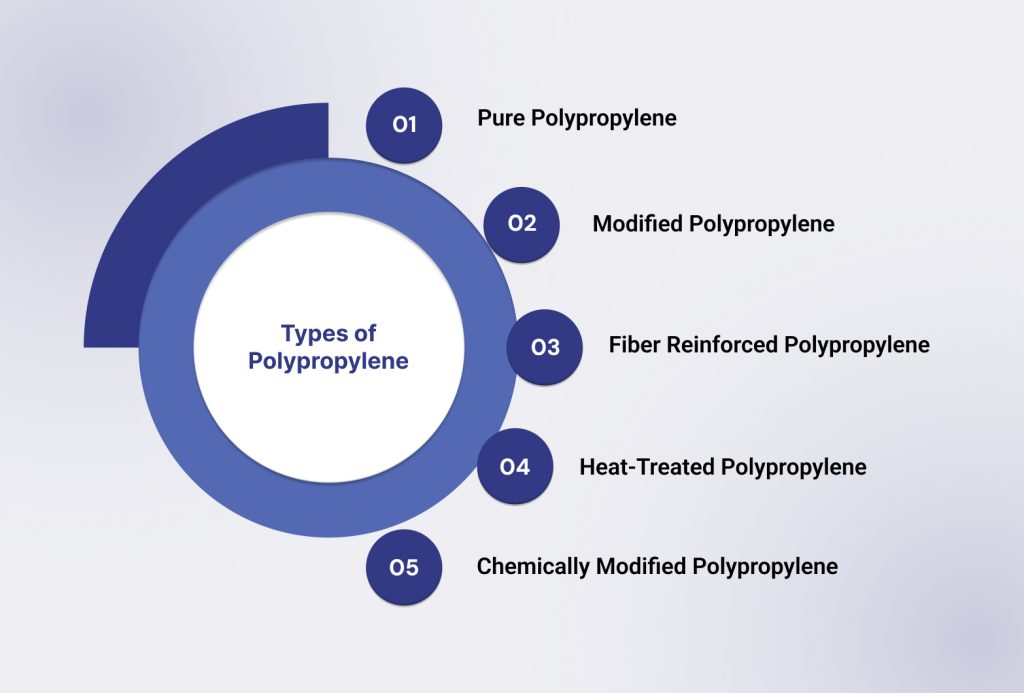
Selecting the right type of PP can significantly impact cost control, performance, and supply chain resilience:
Pure Polypropylene: Transparent and mechanically strong, ideal for applications requiring high durability and environmental resistance.
Modified Polypropylene: Offers heat and impact resistance, suitable for high-temperature industrial components and piping systems.
Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene: High strength and abrasion resistance make it effective for structural applications and high-wear components.
Heat-Treated Polypropylene: Flexible and impact-resistant, commonly applied in thermal shrink films, protective covers, and industrial packaging.
Chemically Modified Polypropylene: Resistant to chemicals and corrosive substances, making it suitable for tanks, piping, and chemical-handling applications.
With an understanding of types and their properties, we can now examine the range of polypropylene products that translate these characteristics into tangible benefits for sourcing and procurement.
Polypropylene Products and Procurement Advantages
The diverse product portfolio of polypropylene provides clear levers for procurement teams to manage cost, performance, and supply chain resilience:
Bags and Packaging Solutions: Strong, reusable, and abrasion-resistant, PP bags protect products while minimizing replacement costs and supply disruptions.
Container Covers and Seals: PP caps and covers safeguard goods such as bottles and cans, ensuring quality and product integrity during storage and transport.
Cups, Plates, and Containers: Durable items for food service and industrial packaging applications, offering both efficiency and resilience.
Thermal Shrink Wraps and Bags: Protect goods from contamination, maintain temperature, and reduce spoilage or damage during transit.
Now, let’s shift our focus to plastics.
What Are Plastics?
Plastics are synthetic or semi-synthetic materials made from polymers that can be molded, shaped, or formed into a wide range of products.
They are among the most widely used materials in manufacturing due to their adaptability, cost-effectiveness, and broad range of applications.
For procurement leaders, program managers, and sourcing executives, understanding the uses, types, and products of plastics enables better decision-making across materials, tooling, and processes, helping to balance costs, supply security, and performance outcomes.
Critical Applications of Plastics
Before selecting a plastic type, it’s essential to understand the scope of its applications. Plastics support a wide variety of industrial, packaging, and consumer uses, providing procurement teams with flexible and reliable material options:
Packaging and Bags: Durable, reusable, and tear-resistant, plastic bags and packaging help maintain product integrity while minimizing supply interruptions and replacement costs.
Covers and Protective Films: Plastic covers and shrink films protect goods during storage and transport, preventing contamination, damage, and spoilage.
Containers, Cups, and Household Items: Durable and versatile, these products are suitable for consumer and industrial applications, offering both practicality and cost efficiency.
Medical and Laboratory Equipment: Plastic components provide chemical resistance and hygiene compliance, supporting critical healthcare and laboratory operations.
Understanding these applications highlights the importance of selecting the right plastic.
Types of Plastics and Their Advantages

Selecting the appropriate type of plastic is a critical lever for sourcing executives. Each plastic type offers distinct performance characteristics, cost considerations, and supply chain implications:
Polyethylene (PE): Flexible, lightweight, and chemically resistant, ideal for packaging, films, and containers.
Polypropylene (PP): Strong, economical, and versatile, widely used in packaging, industrial parts, and medical products.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Durable and corrosion-resistant, suitable for construction materials, piping, and industrial applications.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Rigid and impact-resistant, often used for housings, electronics, and durable components.
Polystyrene (PS): Lightweight and insulating, used for disposable containers, packaging, and insulation materials.
Nylon (PA): High-strength and wear-resistant, suitable for gears, mechanical parts, and high-stress applications.
By understanding plastics’ applications, types, and products, sourcing executives can optimize material selection and supplier engagement. This ensures cost efficiency, supply reliability, and overall program resilience.
Also Read: Plastic Injection Molding: Precision Thermoplastic Components
Now, let’s compare PP directly with plastics to highlight the differences that matter:
Differentiate between Polypropylene and Plastic
Material selection is now a strategic decision in manufacturing and packaging, influencing performance, cost, and sustainability. Polypropylene stands out for its strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance, while other plastics offer varied properties.
The table below highlights the key differences between polypropylene and general plastics across types, properties, and applications.
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | General Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition and Classification | Thermoplastic polymer, semi-crystalline, used in packaging, containers, textiles, medical products | Includes PE, PS, PVC, etc.; classified as thermoplastics or thermosetting plastics |
| Chemical Composition | Repeating propylene monomers (C₃H₆); may include additives | Varies: PE (CH₂), PS (C₈H₈), PVC (C₂H₃Cl); often includes plasticizers and stabilizers |
| Physical Properties | Semi-crystalline, high tensile strength, lightweight, flexible; transparent to translucent | Varies: PE flexible and low strength, PS rigid and brittle, PVC strong but heavy |
| Temperature and Chemical Resistance | Heat-resistant up to 160–170°C; resistant to acids, alkalis, solvents | Varies: PE melts ~115°C, PS ~100°C, PVC can degrade under heat; chemical resistance varies |
| Weight | Lightweight, density ~0.90 g/cm³ | Density varies: PE ~0.94 g/cm³, PS ~1.05 g/cm³, PVC ~1.4 g/cm³ |
| Durability and Fatigue Resistance | High fatigue resistance; bends repeatedly without breaking; stress-cracking resistant | PE moderate, PS brittle, PVC durable but can crack under stress |
| Ease of Processing and Colorability | Easy to mold, extrude, thermoform; easily colored | PE, PS easy; PVC and engineering plastics harder to process; colorability varies |
| Common Applications | Packaging bags, containers, thermal shrink wraps, household products, medical instruments | PE: bottles, films; PS: disposable cups, trays; PVC: pipes, fittings |
| Environmental Impact and Sustainability | Recyclable, lightweight reduces transport energy, lower carbon footprint | Recyclability varies: PE recyclable, PS difficult, PVC problematic |
| Cost and Availability | Cost-effective, widely available, especially for packaging and industrial use | Costs vary: PE low, PS moderate, PVC moderate to high |
Understanding these differences helps you decide when to choose polypropylene or other plastics for your application.
Also read: How to Choose the Right Plastic Product Supplier for Automotive & Industrial Components
How to Choose Between Polypropylene and Plastics?
Selecting the right material is not just an engineering decision. For procurement leaders, sourcing executives, and program managers, it directly impacts cost, supply resilience, and overall program performance. Here are the main considerations:
When to Choose Polypropylene:
Lightweight material that helps reduce transportation or handling costs.
Widely available and economical, helping manage budget volatility in raw material markets.
Durable and fatigue-resistant, suitable for repeated-use or high-stress applications.
Chemically resistant and heat-tolerant for industrial, packaging, or household use.
Recyclable, supporting sustainability goals.
When to Choose General Plastics:
Specific property requirements, such as extreme rigidity (PS), softness (PE), or heavy-duty strength (PVC).
Cost-effective for disposable or single-use applications.
Temperature or chemical resistance is less critical for the application.
Common in films, trays, bottles, pipes, or other specialized products.
Tip: Material selection is both a performance and supply chain strategy. Often, combining polypropylene for durability and other plastics for low-cost or specialized uses balances performance, cost, and supply risk.
Once the material strategy is clear, the next step is working with suppliers who can ensure consistent quality, reliable delivery, and program stability.
Polypropylene vs Plastic: Strategic Material Selection for Manufacturers
For manufacturers, selecting the right material is crucial for ensuring reliable performance, cost efficiency, and sustainability. Choosing between polypropylene (PP) and other plastics can directly influence product durability, production timelines, and overall quality.
JaiRaj Group supports manufacturers in making informed material decisions by focusing on five essential factors that impact long-term outcomes:
1.Material planning and reliability: With expertise in PP, PE, ABS, PC/ABS, nylons, POM, TPEs, and advanced composites, JaiRaj helps OEMs optimize cost, weight, and performance while mitigating raw material fluctuations. In-house R&D enables fast testing of alternatives, giving procurement teams flexibility during market uncertainty.
2. Tooling and mould design optimization: Early engagement in DfM reviews, supported by simulation, reduces tooling errors and accelerates PPAP approval. JaiRaj ensures proper design whether working with PP for lightweight, durable components or other plastics for specialized applications.
3. Process versatility for tailored solutions: From injection and blow moulding to rotational moulding, extrusion, welding, and assembly, JaiRaj provides multiple in-house options. This allows optimal material-process combinations like PP for thermal shrink wraps or structural parts, and ABS or PVC for rigid housings and specialty components.
4. Strategic footprint and operational resilience: With plants in Faridabad, Manesar, Aurangabad, Sanand, and Rudrapur, JaiRaj’s locations near major automotive hubs reduce lead times, cut logistics costs, and provide backup capacity regardless of material type.
5. Proven expertise with varied applications: Over 35 years of experience and certifications including IATF 16949, ISO, and CE make JaiRaj a trusted partner. Its portfolio demonstrates both technical depth and strategic value across materials:
For procurement leaders, JaiRaj Group provides more than just material options. It offers expert guidance that balances performance, cost, and environmental responsibility.
Conclusion
Material selection plays a central role in the success of any product, and the choice between polypropylene and other plastics can influence performance, production efficiency, and sustainability.
The key is to evaluate whether polypropylene’s unique traits suit the specific demands of your application and budget.
Manufacturers that approach this decision strategically often experience three core benefits:
Cost-effective production by using materials that save energy, reduce cycle times, and lower overall material consumption.
High-performing products through materials designed for durability, heat resistance, and chemical stability.
Responsible manufacturing by adopting recyclable materials and minimising waste output.
If you are exploring materials for a new design or reviewing your existing selections, connect with JaiRaj Group for a detailed material assessment or arrange a visit to their facilities at Manesar, Sanand, or Aurangabad.
Get in touch with JaiRaj Group to discuss your project needs.
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between polypropylene and other plastics?
Polypropylene (PP) is a type of thermoplastic, while “plastic” covers many polymers like polyethylene, PVC, and ABS. PP is lightweight, flexible, and chemical-resistant, making it ideal for packaging and automotive parts, whereas other plastics may offer greater rigidity, heat resistance, or impact strength.
2. Is polypropylene stronger than plastic?
Polypropylene (PP) is strong, flexible, and fatigue-resistant, but “strength” depends on the type of plastic. Some plastics like ABS or polycarbonate offer higher impact resistance, while PP excels in chemical resistance and repeated stress applications.
3. Is polypropylene more cost-effective than other plastics?
Yes, PP is generally cheaper due to lower raw material and processing costs. Its low melting point also reduces energy usage during manufacturing. More expensive plastics like polycarbonate or nylon offer higher strength or heat resistance where needed.
4. Can polypropylene be recycled like other plastics?
Yes, PP is recyclable and marked with the code “#5.” It can be reprocessed into automotive parts, containers, and industrial fibers. Recycling availability may vary by region.
5. How does polypropylene handle heat compared to other plastics?
Polypropylene has moderate heat resistance, with a melting point around 160–170°C. It is suitable for applications like dishwasher-safe containers or automotive battery cases. Other plastics, such as polycarbonate or PEEK, can withstand much higher temperatures, making them more appropriate for high-heat environments.
6. What are the environmental considerations when choosing polypropylene?
PP is lightweight and energy-efficient to produce, lowering its carbon footprint compared to heavier plastics. While petroleum-based and non-biodegradable, its durability and recyclability help reduce overall material waste.