Deciding between polypropylene (PP) and ABS is crucial for manufacturers, designers, and procurement teams, as it directly affects product performance, durability, and manufacturing efficiency. The global ABS market is projected to reach $31,204.8 million by 2030, driven by demand in automotive, electronics, and high-durability products.
Engineers must consider tensile strength, flexibility, chemical and moisture resistance, thermal performance, ease of processing, and overall cost to ensure parts meet both functional and economic requirements.
This guide equips product developers and procurement professionals with the insights needed to evaluate polypropylene vs ABS, weigh critical decision factors, and select materials that align with manufacturing methods and application needs.
Key Takeaways:
Polypropylene (PP) is lightweight, flexible, and resistant to chemicals and moisture, making it ideal for automotive parts, food containers, and disposable medical devices.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is rigid, impact-resistant, and heat-stable, suitable for dashboards, electronic housings, and durable consumer products.
PP excels in chemical and moisture resistance and supports cost-efficient, high-volume production, while ABS offers better dimensional stability, machinability, and surface finish.
Use PP for lightweight, flexible, and chemical-resistant components, and ABS when rigidity, impact resistance, and aesthetics are priorities.
Choose PP for lightweight, chemical-resistant, and flexible components, and ABS when rigidity, impact resistance, and polished surface finish are priorities.
Before deciding which material fits your needs, it’s important to understand each in detail.
What is ABS Plastic?
ABS is an opaque thermoplastic made from three monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene. Manufacturers can adjust these monomers to create ABS with specific levels of rigidity, heat resistance, and surface finish, making it highly versatile.
ABS is commonly used in automotive interiors, electronics, household appliances, aerospace components, and medical devices. Its combination of strength, durability, and aesthetic flexibility makes it a top choice for both prototyping and large-scale production.
While ABS emphasizes rigidity and surface quality, polypropylene offers a different value proposition with lightweight, flexible, and chemically resistant characteristics.
Key Applications of ABS
ABS is ideal for parts that require dimensional stability, strength, and design precision:
Automotive Interiors & Exteriors: Dashboards, glove boxes, mirror housings, and grilles use ABS for its rigidity and polished surface finish.
Consumer Electronics: ABS is preferred for TV casings, remotes, and appliance shells due to impact resistance and electrical insulation.
Medical & Laboratory Equipment: Diagnostic devices, surgical instruments, and test kits rely on ABS for durability and precision.
Aerospace Components: Tray tables, seat backs, and instrument panels are manufactured with ABS for complex shapes and tight tolerances.
Household & Industrial Products: Mixers, vacuum cleaners, toys, and housings benefit from ABS’s visual appeal and mechanical strength.
Understanding ABS’s strengths is key, but it’s equally important to examine its limitations before making a material choice.
Advantages of ABS
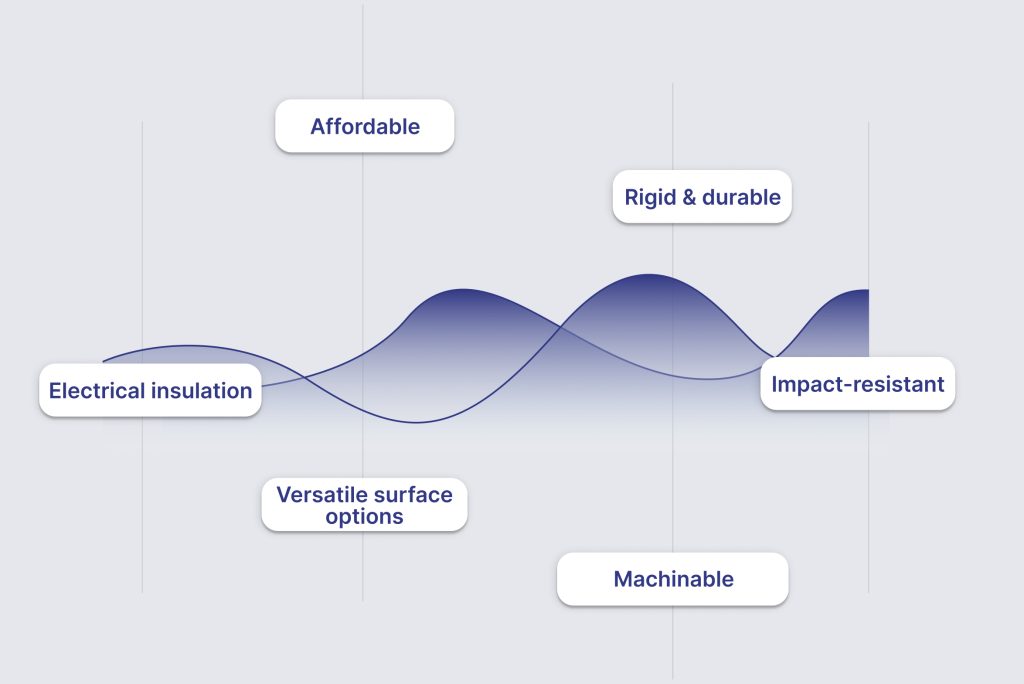
ABS provides a strong combination of cost-effectiveness, durability, and versatility:
Affordable: Cost-effective for high-volume production and prototyping.
Rigid and durable: Maintains structural integrity under repeated use and moderate heat.
Impact-resistant: Withstands shocks, mechanical stress, and abrasion.
Machinable: Supports intricate designs with precise and smooth finishes.
Versatile surface options: Can be polished, textured, or colored to meet aesthetic requirements.
Electrical insulation: Provides reliable non-conductive properties for electronic components.
Despite its benefits, ABS also has some limitations that influence its suitability for certain applications.
Limitations of ABS
ABS may not be ideal for every scenario:
Thermal contraction: ABS experiences slight shrinkage when exposed to heat, affecting dimensional accuracy.
Lower melting point: Not suitable for extremely high-temperature applications or direct flame exposure.
UV sensitivity: Prolonged sunlight can lead to fading, brittleness, and surface degradation.
Flammability: ABS is highly flammable and requires flame-retardant additives for safety compliance.
Non-biodegradable: Must be properly recycled to prevent environmental pollution.
Also read: Automotive Interior & Exterior Plastic Parts Manufacturing: Trends and Innovations in 2025
Now let’s turn to polypropylene (PP), which is lighter, flexible, and highly resistant to chemicals and moisture.
What is Polypropylene (PP)?
Polypropylene (PP) is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic derived from propylene monomers. It stands out for its low weight, flexibility, chemical resistance, and durability, making it suitable for applications from automotive parts to medical disposables and household products.
PP is compatible with injection molding, CNC machining, and industrial 3D printing, Brake & Accelerator Pedals, Plastic Bellows & Struts, making it ideal for both prototyping and large-scale production.
To understand where PP truly excels, it’s important to look at its practical applications.
Key Applications of PP
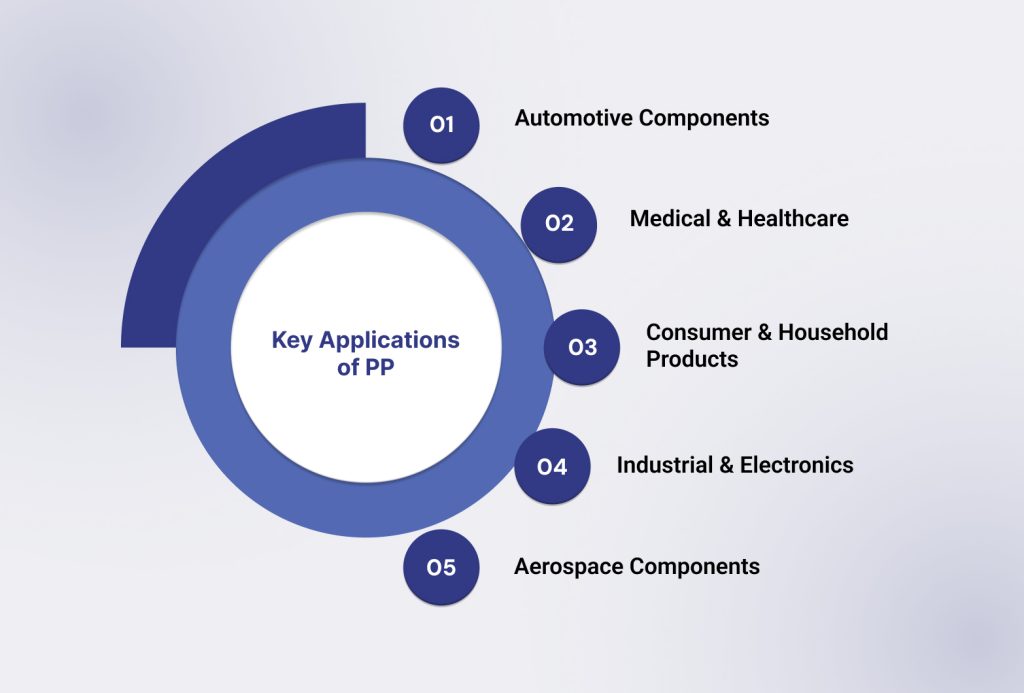
PP performs best where lightweight, flexible, and chemical-resistant materials are required:
Automotive Components: Used in trunk liners, seat panels, bumpers, battery casings, and air ducts for lightweight and durable performance.
Medical & Healthcare: Ideal for single-use syringes, IV port caps, tubing connectors, and other disposable devices due to chemical resistance and sterilization compatibility.
Consumer & Household Products: Applied in food containers, processor bowls, washing machine paddles, and toys for flexibility, durability, and cost-efficiency.
Industrial & Electronics: Suitable for snap-fit housings, duct connectors, and protective casings where toughness and chemical stability are required.
Aerospace Components: Used in trim panels, armrest inserts, cargo liners, and partitions to balance weight, strength, and flexibility.
While PP offers flexibility and moisture resistance, it’s useful to compare it directly with ABS to see which material suits a particular application.
Advantages of Propylene
PP is valued for its resilience, lightweight design, and affordability:
Cost-effective: Generally less expensive than ABS, making it ideal for budget-conscious projects.
Durable and strong: Maintains mechanical integrity and toughness over time.
Lightweight: Low density allows for easy handling and transport of parts.
Flexible: Suitable for snap-fit components, living hinges, and parts requiring bendability.
Chemical and water-resistant: Performs well in exposure to acids, bases, solvents, and moisture.
Heat-resistant: Semi-crystalline structure ensures stability under moderate heat conditions.
Limitations of Propylene
Polypropylene does have some limitations that must be considered for specific applications. Here are some:
Low melting point: Sensitive to high heat and open flames, limiting use in high-temperature environments.
Poor adhesion: Difficult to bond or paint without special surface treatments, increasing production steps.
Non-biodegradable: Requires proper recycling to prevent environmental harm.
Limited UV resistance: Prolonged sun exposure can degrade strength and color.
Dimensional changes: Semi-crystalline structure can cause shrinkage during molding, requiring careful design compensation.
Also read: How to Choose the Right Plastic Product Supplier for Automotive & Industrial Components
Next, let’s discuss side-by-side comparison of ABS and PP.
Difference Between ABS and Polypropylene
ABS and polypropylene (PP) are widely used thermoplastics, each offering distinct strengths, chemical resistance, and thermal performance. Selecting the right material is crucial for part durability, cost efficiency, and application suitability.
The table below summarizes key differences in composition, mechanical and chemical properties, thermal behavior, manufacturability, cost, and typical applications, helping you make an informed choice for your project.
| Property | ABS Plastic | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition & Structure | • Blend of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene • Amorphous structure • Rigid and impact-resistant | • Homopolymer of propylene • Semi-crystalline structure • Tough, flexible, chemical-resistant |
| Mechanical Strength & Rigidity | • High tensile strength: 6,091–7,800 psi • Elongation: 6–40% • Stiff and durable • Suitable for tight-tolerance parts | • Moderate tensile strength: 4,800–7,250 psi • Elongation: 7–100% • Flexible and fatigue-resistant • Ideal for repeated stress applications |
| Chemical Resistance | • Moderate • Sensitive to some solvents • Higher moisture absorption | • Excellent • Resistant to acids, bases, solvents, and water • Hydrophobic; ideal for outdoor use |
| Thermal Properties | • Heat deflection: 138–215°F • Glass transition ~105°C • Lower resistance to continuous heat • May warp under stress | • Heat deflection: 142–210°F • Melting point: 130–171°C • Performs well under sustained heat • Semi-crystalline structure reduces stress cracks |
| Water Absorption & Moisture Resistance | • Absorbs moisture; requires pre-drying for molding | • Hydrophobic • Excellent for waterproof and outdoor components |
| Surface Finish & Aesthetics | • Smooth, polished, and scratch-resistant • Excellent for visible parts | • Softer surface • Less glossy • Better for functional/flexible parts |
| Processing & Manufacturability | • CNC machining, injection molding, 3D printing • Contracts less; tighter tolerances | • CNC machining, injection molding, 3D printing • More shrinkage; semi-crystalline affects mold design |
| Cost & Price Considerations | • Moderate cost • Slightly higher than PP | • Lower cost • Energy-efficient processing and material savings |
| Typical Applications | • Dashboards, instrument panels, enclosures • Consumer electronics • Aerospace interiors | • Bumpers, seat backs, trunk liners • Medical disposables, piping, battery cases • Load floor panels |
| Quick Comparison: Molded, Machined & 3D Printed | • Heat deflection: 215°F molded / 214°F machined / 138°F 3DP • Tensile: 6,091–7,800 psi • Elongation: 6–40% | • Heat deflection: 203°F molded / 210°F machined / 142°F 3DP • Tensile: 4,800–7,250 psi • Elongation: 7–100% |
Next, let’s examine polypropylene and ABS to see which material aligns best with your product requirements and manufacturing goals.
Also Read: Plastic Injection Molding: Precision Thermoplastic Components
Polypropylene vs ABS Plastic: Making the Right Material Choice
Choosing the right plastic is critical for product performance, cost efficiency, and supply reliability. For product designers, sourcing leaders, and manufacturing teams, the decision between polypropylene vs ABS plastic can affect durability, production timelines, and overall quality.
When Polypropylene Makes Sense:
Lightweight and Efficient: Reduces shipping and handling costs while keeping overall product weight low.
Cost-Effective: Widely available and budget-friendly, helping manage raw material price fluctuations.
Durable and Flexible: With excellent fatigue resistance, it performs well under repeated stress or load-bearing applications.
Chemical and Heat Resistance: Suitable for industrial, automotive, and household components exposed to chemicals or moderate heat.
Recyclable: Supports sustainability goals without compromising performance.
When ABS Plastic is the Better Choice:
Impact-Resistant and Rigid: Perfect for structural components, enclosures, and housings that require high mechanical strength.
Aesthetic Surface Finish: Smooth surfaces and easy coloration make it ideal for consumer-facing products.
Precision and Stability: Maintains dimensional accuracy, making it suitable for engineered parts with tight tolerances.
Heat and Wear Resistance: Performs reliably in applications like electronics, appliance panels, and automotive interiors.
Versatile Industrial Use: Commonly used for dashboards, enclosures, protective casings, and equipment components.
Pro Tip: Comparing ABS vs PP is not just about material properties; it’s a strategic choice. Using polypropylene for lightweight, durable applications and ABS for structural, aesthetic, or high-strength parts often achieves the perfect balance of performance, cost, and reliability.
Once your material strategy is defined, collaborating with experienced suppliers ensures consistent quality, timely delivery, and smooth production.
ABS vs PP: A Manufacturer’s Guide to Smart Material Choices
For manufacturers, selecting the right plastic is a critical step in ensuring product performance, cost efficiency, and sustainability. The choice between polypropylene and ABS can significantly influence durability, production timelines, and overall quality.
JaiRaj Group assists manufacturers in making strategic decisions on Polypropylene vs ABS by focusing on five key factors that drive long-term results:
1. Smart Material Planning for Reliable Performance
JaiRaj works with polypropylene, ABS, and other plastics, helping OEMs balance weight, cost, and durability while minimizing the impact of raw material fluctuations. Its in-house R&D enables rapid evaluation of alternatives, giving procurement teams flexibility during market uncertainty.
2. Optimized Tooling and Mold Design
Early involvement in design-for-manufacturing (DfM) reviews, supported by simulation, reduces errors and accelerates PPAP approval. JaiRaj ensures optimal design, whether using polypropylene for lightweight, flexible parts or ABS for rigid, high-strength components.
3. Flexible Manufacturing Processes for Custom Needs
JaiRaj offers diverse manufacturing processes including injection molding, blow molding, extrusion, welding, and assembly. This ensures the best material-process combinations like polypropylene for structural or thermal-resistant parts, and ABS for housings or high-impact components.
4. Strategic Plant Locations for Faster Delivery
With plants in Faridabad, Manesar, Aurangabad, Sanand, and Rudrapur, JaiRaj’s proximity to automotive hubs reduces lead times, lowers logistics costs, and provides backup capacity regardless of the plastic selected.
5. Proven Expertise Across Applications
Over 35 years of experience and certifications including IATF 16949, ISO, and CE make JaiRaj a trusted partner. Its portfolio highlights technical depth and strategic value across plastics:
For manufacturers comparing ABS vs PP, JaiRaj Group provides more than material options. It delivers expert guidance that balances cost, performance, and sustainability, helping you select the right material for your next project.
Conclusion
Choosing the right material between polypropylene and ABS plays a critical role in the success of your product, impacting durability, manufacturing efficiency, and overall cost. The key is to assess whether each material’s properties align with your product’s functional requirements and budget.
Manufacturers who approach the Polypropylene vs ABS decision strategically often benefit in three main ways:
Optimized production costs: Selecting the right plastic reduces energy usage, shortens cycle times, and minimizes material waste.
Enhanced product performance: ABS offers rigidity and impact resistance, while polypropylene provides flexibility and chemical resistance, allowing you to meet specific application needs.
Sustainable manufacturing: Both materials are recyclable, supporting environmentally responsible production while maintaining performance standards.
If you are evaluating materials for a new project or reviewing existing designs, connect with JaiRaj Group for a comprehensive assessment or arrange a visit to their facilities at Manesar, Sanand, or Aurangabad.
Get in touch with JaiRaj Group to determine the right choice between Polypropylene vs ABS for your next product.
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between Polypropylene vs ABS plastic?
Polypropylene is lightweight, flexible, and highly chemical-resistant, while ABS plastic offers higher rigidity, impact resistance, and heat tolerance. Your choice depends on whether your project needs flexibility or structural strength.
2. Which material is better for industrial applications: ABS plastic vs Polypropylene?
ABS plastic is ideal for durable, heat-resistant parts like housings, dashboards, or enclosures. Polypropylene is better for flexible, lightweight components such as caps, hinges, or containers exposed to chemicals.
3. How do ABS vs PP plastics perform in 3D printing and molding?
ABS vs PP behaves differently during manufacturing. ABS plastic provides excellent dimensional stability and is heat-tolerant, while Polypropylene is easier to mold, requires less energy, and is suitable for flexible and fatigue-resistant parts.
4. Which is more cost-effective: ABS plastic vs Polypropylene?
ABS plastic vs Polypropylene differs in cost. Polypropylene is generally cheaper due to lower material and processing expenses. ABS offers mechanical strength and heat resistance, but at a higher price, making it suitable for premium or high-stress parts.
5. How do ABS vs PP plastics handle chemical exposure?
ABS plastic vs Polypropylene reacts differently to chemicals. Polypropylene resists acids, bases, and solvents, making it ideal for chemical containers or industrial tanks. ABS is less chemically resistant but excels in structural and impact-sensitive applications.
6. Can both Polypropylene vs ABS plastic be used for food or medical applications?
Yes, both have food-safe grades. ABS plastic vs Polypropylene is commonly used in machinery parts or housings, while Polypropylene is widely preferred for containers, caps, medical consumables, and other hygiene-sensitive applications.