Choosing between a metal tube and a plastic tube is a critical decision in manufacturing, construction, and fluid transport applications. The global tubing market continues to expand by USD 122.19 billion by 2035 due to rising demand across automotive, infrastructure, packaging, and industrial sectors. Each material offers distinct benefits that impact strength, cost, durability, and ease of installation.
For procurement teams, and manufacturers, the choice between metal and plastic tubes goes beyond basic performance. Factors like corrosion resistance, temperature tolerance, weight, maintenance needs, and overall lifecycle costs influence product reliability and operational efficiency.
This guide outlines the key differences between metal or plastic tube, helping you select the most suitable option for your application.
Key Takeaways:
- Metal tubes offer superior strength, temperature resistance, and structural stability, making them ideal for high-pressure and heavy-duty applications.
- Plastic tubes are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and cost-effective, suitable for fluid transport, packaging, and non-structural use.
- Metals like steel, copper, and aluminum excel in durability and rigidity, while plastics like PVC, PE, and PP provide flexibility, ease of installation, and lower maintenance.
- Metal tubing involves higher upfront costs but provides long-term reliability, while plastic tubing offers affordability and simplified installation.
- The final choice depends on application environment, budget, pressure ratings, and sustainability targets.
To understand which option suits your application, let’s first look at what metal tubing offers.
What is Metal Tubing?
A metal tube is a hollow cylindrical structure made from metals such as steel, stainless steel, aluminum, or copper. Known for their strength, durability, and heat tolerance, metal tubes are widely used in automotive systems, construction frameworks, fluid transport, and heavy machinery.
Manufacturers often use metal tubing in critical components such as Brake & Accelerator Pedals and Shockers & Suspension Components, where structural integrity and resistance to high stress are paramount.
For executives, understanding the properties of metal tubes helps balance performance, cost, and fabrication requirements.
While metal tubes provide high strength and durability, they also come with trade-offs.
Pros and Cons of Using Metal Tubing
Metal tubes are ideal for applications where heat or pressure resistance are critical. They are commonly used in structural frameworks, high-pressure fluid systems, automotive, and industrial machinery.
Here’s a concise overview of the advantages and limitations of using metal tubes:
| Pros | Cons |
| Exceptional strength and rigidity for structural applications | Heavier, which increases transportation and handling costs |
| High durability and long service life | Higher material and fabrication costs |
| Excellent heat and pressure resistance | Requires specialized tools and skilled labor for installation |
| Suitable for load-bearing and high-stress environments | Prone to corrosion if not properly treated or coated |
Knowing the pros and cons of metal tubing helps, but it’s also important to consider its real-world applications.
Key Applications of Metal Tubing
The versatility of metal tubes supports a wide range of industries:
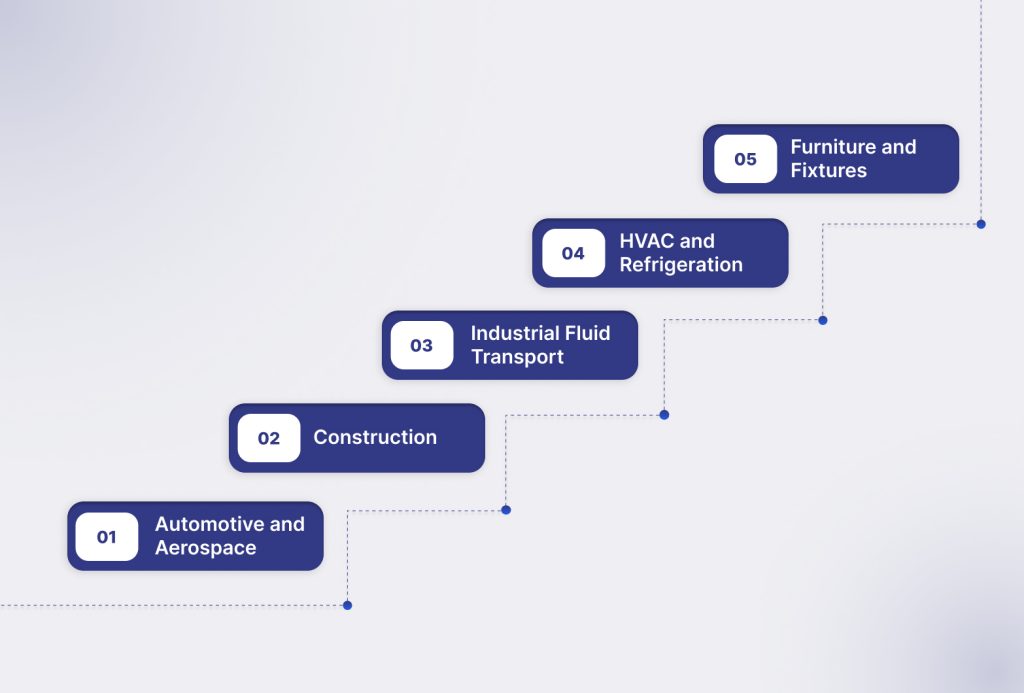
- Automotive and Aerospace: Used in hydraulic lines, Shockers & Suspension Components, and structural frames due to high pressure and temperature tolerance.
- Construction: Steel and aluminum tubes are used in frameworks, supports, and pipelines, providing strength and stability.
- Industrial Fluid Transport: Ideal for high-pressure steam, gases, or chemicals where plastic may fail.
- HVAC and Refrigeration: Copper tubes are preferred for their thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance.
- Furniture and Fixtures: Metal tubes offer sleek aesthetics and long-lasting performance.
Next, let’s explore plastic tubing, which offers a different set of benefits, particularly for lighter and cost-sensitive applications.
Ensure reliable metal and plastic tube applications in critical components, such as Precision Components from Advance Polymers or Braking System Components, with JaiRaj Group’s engineered solutions and proven manufacturing expertise.
What is Plastic Tubing?
Plastic tubes are hollow structures made from polymers like PVC, PE, PP, or nylon. They offer lightweight construction, corrosion resistance, and flexibility, making them ideal for fluid transport, packaging, and various industrial uses.
In automotive interiors, plastic tubing often supports Mobility Plastic Seating Solutions, Interior & Exterior Accessories, and protective covers for Brake & Accelerator Pedals. Plastic tubing is also a popular choice in medical, irrigation, and consumer applications where weight, maintenance, and ease of installation are critical.
To make an informed choice, it’s crucial to weigh both the advantages and limitations of plastic tubing.
Advantages and Limitations of Plastic Tubing
Plastic tubes provide lightweight, flexible, and corrosion-resistant solutions. They are preferred in fluid transport, irrigation, packaging, and non-structural applications where cost efficiency and ease of installation are priorities.
The following table summarizes the benefits and limitations of plastic tubing:
| Pros | Cons |
| Lightweight and easy to handle, reducing transportation costs | Lower strength and rigidity compared to metal |
| Corrosion-resistant and chemically stable | Limited heat and pressure tolerance |
| Flexible, allowing easier installation in tight spaces | Can degrade under UV exposure or prolonged stress |
| Cost-effective for both permanent and temporary applications | Shorter lifespan under demanding conditions |
With the benefits and limitations clear, it’s useful to see how plastic tubes are applied across industries.
Critical Applications of Plastic Tubing
Plastic tubes are widely used across industries:
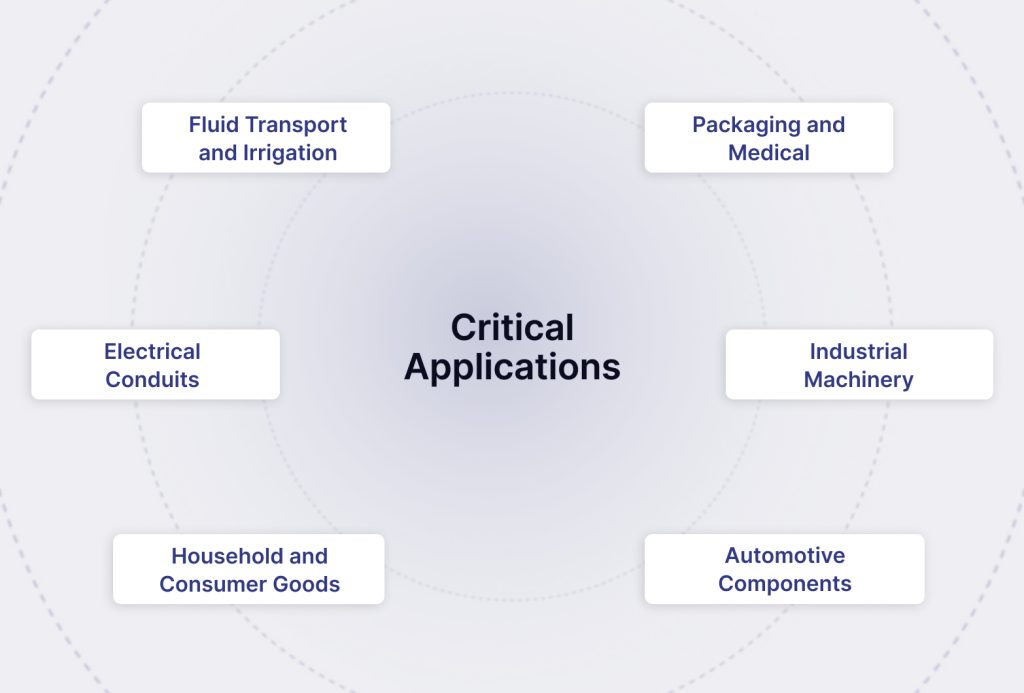
- Fluid Transport and Irrigation: Lightweight and flexible for water supply, agricultural irrigation, and drainage.
- Packaging and Medical: Used in IV lines, protective covers, and food packaging due to chemical resistance and hygiene standards.
- Electrical Conduits: Plastic tubes like PVC provide insulation and protect wires from environmental damage.
- Industrial Machinery: PE and nylon tubes are used for air, fuel, and chemical transfer in controlled environments.
- Household and Consumer Goods: Common in piping, furniture, garden tools, and lightweight frameworks.
- Automotive Components: Supports Interior & Exterior Accessories, Plastic Bellows & Struts, and elements of Mobility Plastic Seating Solutions.
After reviewing applications, comparing key factors between metal and plastic tubing can guide material selection.
Also Read: Plastic Injection Molding: Precision Thermoplastic Components
Factors to Consider While Choosing Metal and Plastic Tubing
Deciding on the right tubing material goes beyond basic cost comparison. The choice between metal and plastic tubes affects structural performance, production efficiency, maintenance requirements, and overall project economics.
The table below highlights the key differences:
| Property | Metal Tube | Plastic Tube |
| Material Composition | Steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, brass | PVC, PTE, PPCP, ABS, PTFE, Nylon |
| Strength & Rigidity | Very high, suitable for structural and high-pressure uses | Moderate to low; flexible and lightweight |
| Temperature Resistance | Excellent; withstands high heat and cold | Limited; most soften or deform at high temperatures |
| Corrosion Resistance | Varies: stainless and copper are resistant, others may need coating | Excellent; inherently corrosion-resistant |
| Weight | Heavy, increases handling and transport costs | Light, easy to handle and install |
| Cost | Higher upfront material and fabrication costs | More economical, especially for large installations |
| Processing & Installation | Requires welding, threading, or bending equipment | Easy to cut, join, and install without specialized tools |
| Lifespan & Durability | Long lifespan in demanding environments | Shorter lifespan under extreme conditions |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable metals; high embodied energy | Lightweight and recyclable (varies by type); lower transport energy |
| Common Applications | Construction, automotive, HVAC, high-pressure piping | Irrigation, packaging, consumer goods, low-pressure fluid systems |
Also read: How to Choose the Right Plastic Product Supplier for Automotive & Industrial Components
Based on these factors, here’s when you should consider each material.
How to Choose Between Metal and Plastic Tubes?
Choosing the right material is more than a technical decision. For procurement leaders, sourcing teams, and manufacturing planners, it directly affects cost control, supply stability, and overall operational performance.
Below are the key factors to guide your decision.
When to Choose Metal Tubes:
- High structural strength and rigidity are required for critical systems.
- Applications involve elevated temperature or pressure conditions.
- Long-term durability, reliability, and minimal maintenance are priorities.
- The system includes load-bearing or high-stress components such as hydraulic lines or structural frames.
- Corrosion protection is needed, achievable through stainless steel or appropriate coatings.
When to Choose Plastic Tubes:
- Lightweight and flexible installations are required to simplify handling and reduce transportation costs.
- Chemical resistance and corrosion protection are important for the application.
- The system operates under moderate temperature and pressure levels.
- Non-structural or fluid transfer applications such as irrigation, packaging, or cable protection are involved.
- Easy installation, cost efficiency, and faster project timelines are key priorities.
Tip: Many manufacturers use a combination of metal and plastic tubing, metal tubes for strength and temperature-critical areas, and plastic tubes for lightweight, low-cost fluid distribution.
Also read: Automotive Interior & Exterior Plastic Parts Manufacturing: Trends and Innovations in 2025
Metal vs Plastic Tubes: Strategic Material Selection for Manufacturers
For manufacturers, choosing the right material is essential to achieve reliable performance, cost efficiency, and long-term sustainability. Deciding between a metal or plastic tube impacts weight, fabrication methods, operational flexibility, and overall production quality.
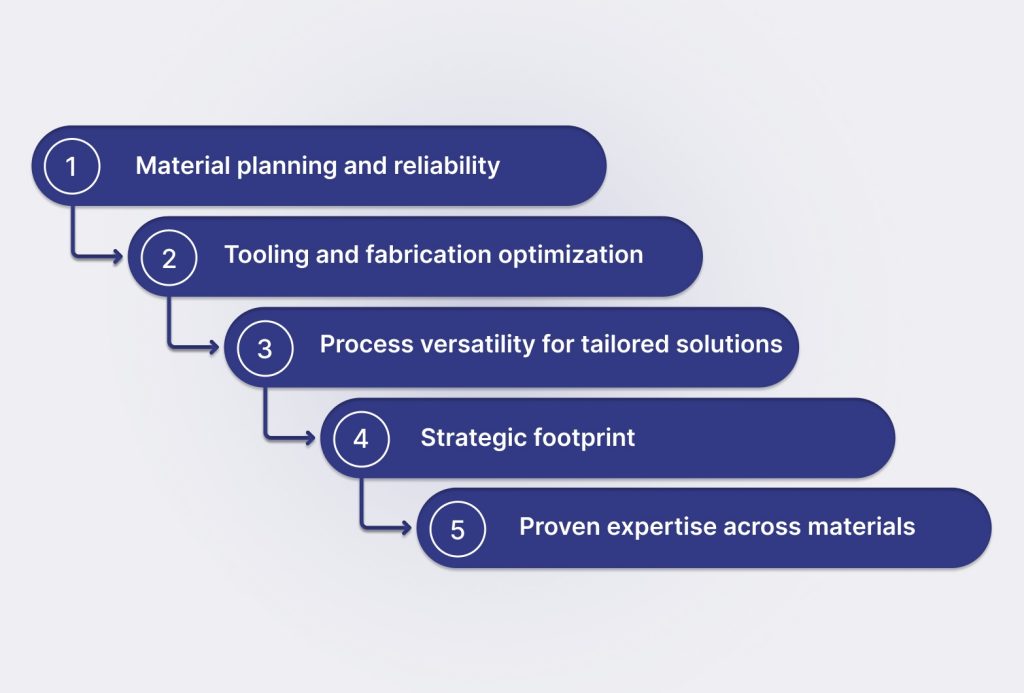
JaiRaj Group helps manufacturers make informed material choices by focusing on five key strategic factors that influence successful outcomes:
1. Material planning and reliability
By combining metal and plastic tube solutions, JaiRaj helps manufacturers balance weight, cost, and raw material availability. Strong sourcing capabilities and technical expertise support better planning during periods of market uncertainty.
2. Tooling and fabrication optimization
Early involvement in design and manufacturing reviews ensures precise welding, molding, or joining. This approach reduces errors and shortens production timelines, regardless of the material selected.
3. Process versatility for tailored solutions
JaiRaj provides multiple fabrication options such as extrusion for plastic tubes and bending or forming for metal tubes. This versatility supports varied design needs and ensures each application receives the most suitable process.
4. Strategic footprint and operational resilience
With facilities in Faridabad, Manesar, Aurangabad, Sanand, and Rudrapur, JaiRaj ensures steady supply, reduced lead times, and strong logistics support to keep production schedules on track.
5. Proven expertise across materials
With over 35 years of experience and certifications including IATF 16949, ISO, and CE, JaiRaj provides practical recommendations for mixed-material strategies.
Their portfolio reflects deep knowledge in both metal and plastic tube applications across automotive and industrial sectors.
- Brake & Accelerator Pedals
- Mobility Plastic Seating Solutions
- Shockers & Suspension Components
- Plastic Bellows & Struts
- Interior & Exterior Accessories
- Precision Components from Advanced Polymers
For procurement and manufacturing leaders, JaiRaj Group provides more than just materials. It offers strategic support that aligns performance requirements with cost efficiency and environmental goals
Conclusion
Choosing the right material between a metal or plastic tube plays a crucial role in product performance, installation efficiency, and overall lifecycle cost. The key is to match each material’s properties with your project’s functional needs and budget.
Manufacturers who approach the metal vs plastic tube decision strategically often see clear advantages:
- Optimized project costs: Plastic tubes are easier to handle and install, while metal tubes reduce long-term replacement expenses in demanding setups.
- Improved performance: Metal tubes offer superior strength and temperature resistance, whereas plastic tubes deliver flexibility, corrosion resistance, and ease of customization.
- Sustainable choices: Metal tubes are fully recyclable and long-lasting, while plastic tubes lower energy use during production and transportation.
If you’re evaluating materials for a new system or upgrading existing infrastructure, connect with JaiRaj Group for a detailed material assessment or visit their facilities in Manesar, Sanand, or Aurangabad.
Get in touch with JaiRaj Group to find the right balance between metal or plastic tube solutions for your application.
FAQs
1. What factors should you consider when choosing between a metal or plastic tube?
Key factors include strength requirements, temperature exposure, budget, environmental conditions, and intended application.
2. When is a metal tube the better choice?
Metal tubes are ideal for high-pressure systems, structural support, and applications involving extreme temperatures or heavy loads.
3. When does a plastic tube make more sense?
Plastic tubes work well for low-pressure systems, cost-sensitive projects, and situations where corrosion resistance and flexibility are priorities.
4. How do installation and maintenance compare between the two?
Plastic tubes are lighter and easier to install, reducing labor time. Metal tubes need more support but generally offer longer service life with less frequent replacement.
5. Which option performs better in harsh environments?
Metal tubes withstand heat and mechanical stress better. Plastic tubes resist chemical corrosion and moisture, making them suitable for damp or chemical-heavy settings.
6. How do cost and lifecycle expenses differ?
Plastic tubes are cheaper upfront, while metal tubes may offer better long-term value due to durability and lower replacement frequency.
7. Are both metal and plastic tubes environmentally sustainable options?
Metal tubes are fully recyclable and durable. Plastic tubes require less energy to produce and are lighter to transport, reducing emissions, though recyclability depends on the material type.